2. 广西科学院非粮生物质技术全国重点实验室,广西南宁 530007
2. National Key Laboratory of Non-food Biomass Energy Technology, Guangxi Academy of Sciences, Nanning, Guangxi, 530007, China
红树林是地处热带和亚热带地区的独特潮间带生态系统,具有高盐分、强还原、密潮汐、矿物质富饶等独特的生态环境,被誉为“海上的森林”[1, 2]。特殊生存环境中的真菌作为一类新型的微生物资源,其生存环境特殊(特境)或生存策略(环境适应或物种间互作机制)的特殊性使其具备了独特的代谢和防御系统,进而可以产生结构独特新颖的次级代谢产物,已被证实是新型药物先导化合物发现的重要优质源泉。红树林来源真菌作为特殊生境的一大类群,其生理生化特点更加鲜明,次级代谢产物合成更具特色。因此,对广西红树林来源真菌所产生的先导化合物的研究必将提高北部湾海洋资源的利用度,加快海洋药物开发的步伐。红树林来源真菌次级代谢产物中存在一系列结构新颖、活性良好的生物活性化合物,包括生物碱、聚酮类、肽类、萜类、蒽醌等[3-5]。其中生物碱类化合物不仅具有十分独特和复杂的化学结构,而且还表现出较强的抗肿瘤、抗病毒、抗菌和抗炎等多种生物活性,因此在医药及天然产物开发研究等众多领域中具有广阔的应用前景[6, 7]。
一般情况下,氨基酸的氮原子的数量、位置和碳骨架的类型是影响生物碱类型的重要因素。因此,本文以氨基酸前体为依据对生物碱进行分类,在前人研究的基础上综述了从2015-2021年红树林来源真菌中发现的116个新生物碱类化合物,包括鸟氨酸系生物碱17个、色氨酸系生物碱48个、苯丙氨酸系生物碱4个、邻氨基苯甲酸系生物碱6个、二酮哌嗪类生物碱28个和其他类生物碱13个,并对这些化合物的结构和活性进行了介绍,拟为红树林来源真菌生物碱类次级代谢产物的研究提供参考。
1 鸟氨酸系生物碱鸟氨酸系生物碱主要是由L-鸟氨酸参与合成的一类生物碱。在不同生物中,L-鸟氨酸的合成途径有所不同:在动物体内,L-鸟氨酸由L-精氨酸在精氨酸酶的催化下生成;在植物中,L-鸟氨酸主要由L-谷氨酸生成;在微生物体内,L-鸟氨酸主要以谷氨酸为前体,经历多步酶促反应生成。
红树林来源真菌主要通过L-鸟氨酸来合成吡咯烷类生物碱和吡咯里西啶类生物碱。Wang等[8]从海南东寨港红树林树根分离到的枝孢属真菌Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1中发现了两种新的含琥珀酰亚胺衍生物Cladosporitins A (1)和B (2),化合物2对人肝癌细胞株BEL-7042、人慢性髓原白血病细胞株K562和人胃癌细胞株SGC-7901均有细胞毒性,细胞半抑制浓度(即某一物质诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡达到50%效果时的浓度,IC50值)分别为(29.4±0.35)、(25.6±0.47)、(41.7±0.71) μmol/L。Cui等[9]从红树林内生真菌花斑曲霉Aspergillus versicolor SYSU-SKS025中分离得到一对自然界中较罕见的3-芳基异喹啉酮对映体:(+)-asperglactam A (3)、(-)-asperglactam A (3),并对其进行α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性评估,结果显示这对对映异构体对α-葡萄糖苷酶均具有中等抑制活性,IC50值为50-190 μmol/L。Yang等[10]从南海红树林轮层炭菌属真菌Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ001提取物中获得一种新的细胞松弛素代谢物[11]-细胞松弛素-5(6), 13-二烯-1, 21-二酮-7, 18-二羟基-16, 18-二甲基-10-苯基-(7S*, 13E, 16S*, 18R*)(4),该化合物对大肠杆菌Escherichia coli、金黄色葡萄球菌Staphylococcus aureus和蜡样芽胞杆菌Bacillus cereus的抗菌活性较弱,对副溶血性弧菌Vibrio parahaemolyticus和溶藻弧菌Vibrio alginolyticus的最小抑制浓度(MIC)相同,均为50 μg/mL。Guo等[11]从红树林植物根际土壤帚枝霉属真菌Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112中分离到两个新的环二肽类化合物Saroclides A和B (5和6),化合物5、6对5种癌细胞和4种致病微生物均无活性,但化合物5具有降脂作用。Wang等[12]从海南省东寨港红树林保护区采集到的木果Xylocarpus granatum树茎的内生炭角菌属真菌Xylaria sp.HNWSW-2中发现了一种新的细胞松弛素衍生物Xylarisin B (7),但该化合物没有明显的乙酰胆碱酯酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。Chen等[13]从红树林内生篮状菌属真菌Talaromyces sp. HZ-YX1中获得一种特殊的生物碱Talaramide A (8),该化合物是第2个具有独特氧化三环系统的生物碱,它对分枝杆菌Mycobacterium PknG有较好的抑制作用,IC50值为55 μmol/L。Ding等[14]从2种红树林真菌(菌株K38和E33)的共培养液中分离出一种新的Nonadride衍生物(-)-byssochlamic acid imide (9),生物活性测定初步表明化合物9对禾谷镰刀菌Fusarium graminearum具有一定的体外抗真菌活性。Qi等[15]从福建省集美红树林根际土壤中分离得到弯孢聚壳属真菌Eutypella scoparia 1-15,并从这些菌株中分离得到两个新化合物Scoparasin C (10)和Scoparasin D (11),其中化合物11对4种癌细胞株(包括A375、A549、HepG2和MCF-7)表现出有效的细胞毒性,IC50值为1.08-3.51 μmol/L。Meng等[16]从红树林植物内生青霉菌Penicillium brocae MA-231中分离得到一种新的多羟基二氢吡喃[2, 3-c]吡咯-4, 5-二酮衍生物Pyranonigrin F (12),该化合物对广谱的人类、水生和植物病原体均表现出显著的生物活性。Zhou等[17]从红树林植物内生青霉菌Penicillium sp.GD6中分离得到一种新的吡咯里西啶类生物碱Penibruguieramine A (13),该生物碱具有一种全新的1-烯丙基-2-甲基-8-羟甲基吡咯烷-3-酮骨架结构。Wang等[18]从福建省红树林秋茄树Kandelia obovata根际土壤中分离得到枝顶孢霉属真菌Acremonium citrinum. MMF4,并从该真菌培养产物中获得一个新化合物Dietziamide C (14),该化合物是一个内消旋体;对化合物14进行HeLa细胞株的细胞毒性试验,结果显示该化合物对HeLa细胞株的IC50值>40 μmol/L。Li等[19]从两株海洋曲霉属真菌Aspergillus versicolor IMB17-055和Aspergillus chevalieri IMB18-208的共培养产物中挖掘新的抗菌代谢物,从中分离得到已知的主产物Burnettramic acid A和3个新的吡咯里西啶类化合物Burnettramic acids C-E (15-17),3个新化合物均对白色念球菌Candida albicans、新月弯孢菌Curvularia lunata、镰刀菌属Fusarium sp.和链格孢菌Alternaria sp.表现出显着的抗真菌活性,MIC值为0.5-64.0 μg/mL。化合物1-17的结构如图 1所示。
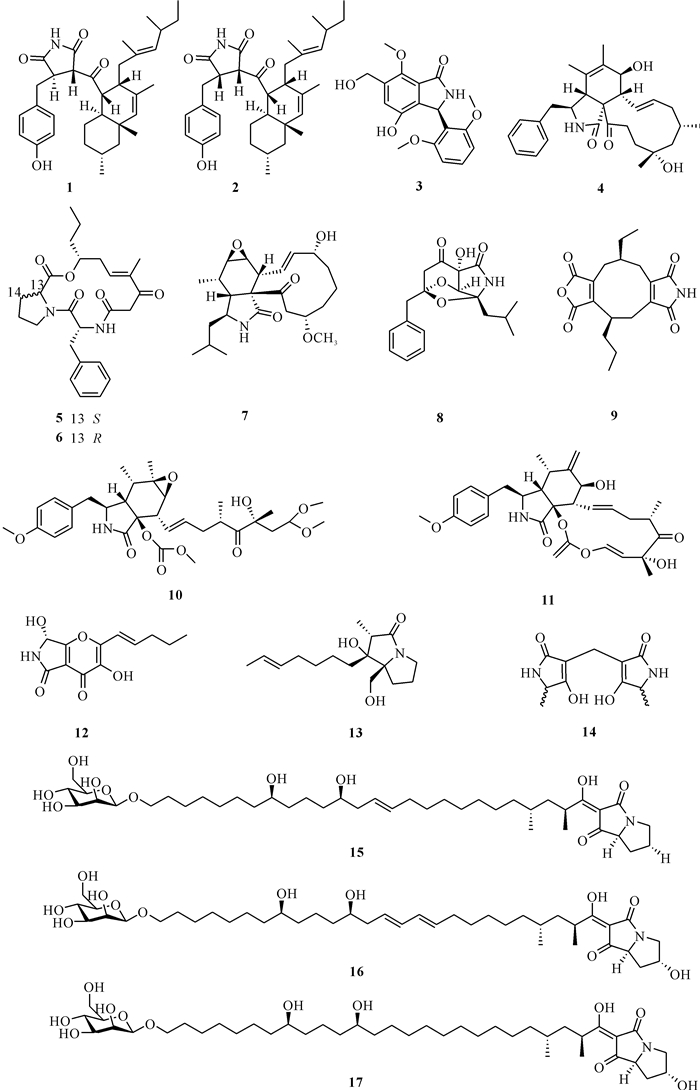
|
| 图 1 化合物1-17的结构 Fig.1 Structures of compounds 1-17 |
2 色氨酸系生物碱
L-色氨酸是含有吲哚环结构的芳香氨基酸,经莽草酸途径由邻苯基苯甲酸合成而来,是众多吲哚类生物碱的合成前体。Zhang等[20]从青霉菌Penicillium sp.L129中分离得到一种新型L-色氨酸来源的生物碱Quinadoline D (18); 进一步采用噻唑蓝(MTT)法检测化合物对MCF-7、A549、U87和PC3癌细胞株的细胞毒性,同时还研究了该化合物的抑菌活性,结果显示Quinadoline D (18)没有明显的抗癌抗菌活性。Yu等[21]从红树林根部内生新萨托菌属真菌Neosartorya udagawae HDN13-313中分离得到两个新化合物Neosartoryadins A (19) 和B (20),它们均具有独特的6/6/6/5喹唑啉四环结构,并表现出抗甲型H1N1流感病毒的活性,IC50值分别为66、58 μmol/L。Zhang等[22]从青霉菌Penicillium oxalicum EN-201中分离鉴定了一种新的、具有哌啶结构的异戊二烯化吲哚衍生物Penioxamide A (21),化合物21在双环[2.2.2]重氮辛烷环上具有罕见的反向相对构型,并表现出较强的卤虫致死活性,半数致死量(LD50)值为5.6 mmol/L。Zheng等[23]从红树林根际土壤来源微紫青霉菌Penicillium janthinellum HK1-6中分离到一种新的异戊二烯吲哚生物碱,命名为Paraherquamide J (22); 对化合物22进行卤虫致死活性检测, 未发现其有明显活性。Li等[24]从红树林来源青霉菌Penicillium sp.IMB17-046中发现了一种新的吡嗪衍生物Trypilepyrazinol (23); Trypilepyrazinol (23)具有广谱抗病毒活性,包括人类免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)、丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)和甲型流感病毒(IAV),IC50值为0.5-7.7 μmol/L,同时还显示出对幽门螺杆菌Helicobacter pylori的抗菌活性,MIC值为1-16 μg/mL。Li等[25]从红树林沼泽沉积物来源的青霉菌Penicillium raistrickii IMB17-034中分离得到化合物Raistrickindole A (24)和Raisstrickin (25),Raistrickindole A (24)是一种新的吲哚类生物碱,含有一个特殊的吡嗪[1′,2′: 2,3]-[1, 2]恶嗪[6,5-b]吲哚四异环系统,Raisstrickin (25)是一种新的苯并二氮杂卓衍生物,化合物24和25均具有抗HCV活性。Zheng等[26]从红树林海榄雌Avicennia L.根部来源的正青霉菌Eupenicillium sp. HJ002中分离得到3个新的吲哚二萜Penicilindoles A-C (26-28),其中Penicilindole A (26)对人A549和HepG2细胞株具有细胞毒活性,IC50值分别为5.5、1.5 μmol/L。Yang等[27]从三亚采集的红树林来源青霉菌Penicillium sp.SCSIO041218的次级代谢产物中发现了4种新的异戊烯基吲哚生物碱Mangrovamide D-G (29-32)。Cui等[28]从一株红树林内生间座壳属真菌Diaporthe phaseolorum SKS019分离得到4种新的色烯并[3,2-c]吡啶Diaporphasines A-D (33-36),这些化合物是首次从该属植物中分离得到的生物碱成分,并且化合物Diaporphasines A-D (33-36)是具有独特的色烯并[3,2-c]吡啶核的生物碱的第3次报道。Cui等[29]从红树林来源间座壳属真菌Diaporthe sp. SYSUHQ3中分离得到两个新的异戊二烯异吲哚生物碱Diaporisoindoles A (37)、B (38)和一个罕见的二异戊二烯异吲哚二聚体Diaporisoindole C (39),其中Diaporisoindole A (37)表现出对结核分枝杆菌Mycobacterium tuberculosis蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶B的抑制活性,IC50值为4.2 μmol/L。Zhu等[30]从一种半红树林植物中分离得到青霉菌Penicillium chrysogenum V11,并从该菌中发现了一个特殊的6/5/6/5/6/13稠环系统的新化合物Penochalasin K (40),化合物40对炭疽病菌Colletotrichum gloeosporioides和丝核菌Rhizoctonia solani均表现出显著的抑制活性,MIC值分别为6.13、12.26 μmol/L,并对MDA-MB-435、SGC-7901和A549细胞株表现出显著的细胞毒性(IC50<10 μmol/L)。Gao等[31]从红树林植物红海兰Rhizophora stylosa Griff.的新鲜内部组织中分离出的一株内生毛霉菌属真菌Mucor irregularis QEN-189中发现了20种结构多样的吲哚二萜,包括6种新化合物Rhizovarins A-F (41-46),其中化合物41-43是所报道的吲哚二萜中结构最复杂的化合物。对这些化合物进行HL-60和A-549癌细胞株的抗肿瘤活性评价,结果表明化合物41、42对HL-60和A549癌细胞株有抑制活性,而化合物45只对A549癌细胞株有抑制活性[31]。Huang等[32]从一种半红树林药用植物中发现了青霉菌Penicillium chrysogenum V11,并从该菌株中分离得到两种新的球毛壳菌素Penochalasin I (47)和Penochalasin J (48),化合物47具有全新的6/5/6/5/6/13稠环系统,它是球毛壳菌素类化合物中具有C-5和C-20连接六环结构的第一个化合物,且对MDA-MB-435和SGC-7901细胞株具有明显的细胞毒性(IC50<10 μmol/L);化合物48对梭状芽孢杆菌Clostridium prazmowski有显著的抑制活性(MIC=23.58-47.35 μmol/L)。Cai等[33]从红树林植物卤蕨Acrostichum aureum的根际土壤中分离得到曲霉属真菌Aspergillus taichungensis ZHN-7-07,并从该菌中发现了3种新的吲哚二酮哌嗪生物碱Okaramines S-U (49-51),其中化合物49和50是异戊二烯化的吲哚二酮哌嗪生物碱;Okaramine S (49)对HL-60细胞株表现出显著的细胞毒活性,IC50值为0.78 mmol/L。Chen等[34]从红树林内生季也蒙酵母菌Meyerozyma guilliermondii中分离得到两种新的异吲哚啉酮Meyeroguillines A和B (52和53)。Meng等[35]从泰国红树林根际土壤散囊菌属真菌Eurotium rubrum MA-150的提取物中分离出3种新的异棘豆素型吲哚二酮哌嗪生物碱Rubrumazines A-C (54-56)。对化合物进行盐水虾致死活性评价,其中化合物54和56有较好的活性,LD50值为9.85-29.8 μmol/L。Lv等[36]从海洋曲霉属真菌Aspergillus sp.WHUF03110的乙酸乙酯提取物中分离得到一种新的色喹啉类似物Asperdiazapinone G (57),但该化合物对10种革兰氏阴性菌、7种革兰氏阳性菌以及耻垢分枝杆菌Mycobacterium smegmatis ATCC 607、白色念珠菌Monilia albicans ATCC SC5314、白色念珠菌Monilia albicans y-1-4均无抑制活性。Cao等[37]从海南省东寨港红树林根际土壤来源枝孢属真菌Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1中分离到一种新的β-碳碱衍生物Cladospomine (58),但化合物58对HeLa、BEL-7402、K562和SGC-7901细胞株没明显的细胞毒性,也无α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。Chen等[38]从红树林海棠Xylocarpus granatum根部内生青霉菌Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025中分离得到一种天然稀有的生物碱-N-氧化物:N-(6-羟基-2-氧代吲哚啉-3-基烯)-5′-甲氧基-5′-氧代丁基氧化胺[N-(6-hydroxy-2-oxoindolin-3-yli-dene)-5′-methoxy-5′-oxobutyl-amine oxide](59),该化合物无明显的抗菌活性和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。Chen等[39]从红树林内生真菌拟茎点霉属Phomopsis sp.33#中分离得到4种新的色烯吡啶衍生物Phochrodines A-D (60-63),化合物60-63具有不寻常的5H-色烯[4,3-b]吡啶骨架,是发现的第一个天然存在的色烯吡啶。对这些化合物进行抗炎、抗氧化和细胞毒性的活性评价,结果表明化合物62和63对一氧化氮有中等抑制活性,IC50值分别为49.0、51.0 μmol/L,化合物63对DPPH自由基具有较好的清除能力,IC50值为34.0 μmol/L[39]。Zheng等[40]从一株来自于南海红树林植物的曲霉属真菌Aspergillus sp.33241的菌丝体中发现了一种新的芦马嗪肽Aspergilumamide A (64)。Li等[41]在海南红树林内生青霉菌Penicillium 299#中发现了一种新的含末端氰基的苯二氮类生物碱(65),该化合物对5株人肿瘤细胞株的体外细胞毒活性均为阴性。上述色氨酸系生物碱由于其结构的复杂性,往往具有良好的生物学活性,在生物合成途径和新酶的发现中具有深入研究的价值。化合物18-65的结构见图 2。

|
| 图 2 化合物18-65的结构 Fig.2 Structures of compounds 18-65 |
3 苯丙氨酸系生物碱
Zhou等[42]从药用红树林植物角果木Ceriops tagal中分离得到的青霉菌Penicillium herquei JX4对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有明显的抑制活性。另外,还从其生物活性提取物分离得到两对对乙酰氨基酚衍生物Penicilqueis A-D (66-69),Penicilqueis A-D (66-69)是首次分离到的、具有新骨架的对乙酰氨基酚衍生物,且这些化合物对白菜黑斑病菌Alternaria brassicicola、番石榴疫病Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae、辣椒炭疽菌Colletotrichum capsici和水稻胡麻斑菌Bipolaris oryzae等9种植物病原真菌和α-葡萄糖苷酶具有广谱的抗真菌活性[42]。化合物66-69的结构如图 3所示。

|
| 图 3 化合物66-69的结构 Fig.3 Structures of compounds 66-69 |
4 邻氨基苯甲酸系生物碱
邻氨基苯甲酸是L-色氨酸生物合成过程中的一个关键中间体,可参与吲哚类生物碱的合成。Chen等[43]从广东省湛江红树林马齿苋Portulaca oleracea根际来源青霉菌Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025中分离到6个新的4-喹诺酮生物碱,其中包括4种外消旋混合物(±)-Oxypenicinolines A-D (70-73)以及Penicinolines F (74)和G (75),化合物(±)-Oxypenicinolines A-D分别含有一个(±)-氧青霉烯醛和一个特殊的6/6/5/5四环体系,该四环结构包含有罕见的四氢吡咯基结构。(±)-Oxypenicinolines A对α-葡萄糖苷酶的IC50值为317.8 μmol/L,高于阿卡波糖(461.0 μmol/L);进一步的分子对接研究表明,(±)-Oxypenicinolines A可能是通过氢键相互作用与α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性位点结合[43]。化合物70-75的结构如图 4所示。

|
| 图 4 化合物70-75的结构 Fig.4 Structures of compounds 70-75 |
5 二酮哌嗪类生物碱
二酮哌嗪类生物碱(Diketopiperazine alkaloids,DKPs)主要是由2个氨基酸通过肽键缩合而成的环二肽(Cyclic dipeptides),稳定的六元环骨架结构使DKPs在药物化学中成为一个重要的药效团,表现出多种生物活性与药理活性。Li等[44]从红树林来源帚枝霉属真菌Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-84中分离出3种新的二酮哌嗪衍生物,即Saroclaazines A-C (76-78)。Saroclaazines A-B (76和77)具有游离酰胺结构,该结构首次发现于含硫芳族DKPs中;对新化合物(76-78)进行HeLa细胞株细胞毒活性测试,结果显示化合物77的IC50值为4.2 μmol/L。Meng等[45]从红树林植物内生青霉菌Penicillium brocae MA-231中发现了4个新二酮哌嗪类化合物:Spirobrocazines A-C (79-81)和Brocazine G (82),化合物82对顺铂耐药的人卵巢癌细胞具有较强的细胞毒性,对致病性金黄色葡萄球菌具有较强的抗菌活性。Meng等[46]从红树林植物的新鲜组织中分离出青霉菌Penicillium brocae MA-231,并从该菌株中发现5种新型硫化二酮哌嗪衍生物Penicibrocazines A-E (83-87),对分离得到的化合物进行9种肿瘤细胞株的细胞毒活性评价,结果表明化合物83-86对部分菌株具有一定的抑菌活性。Zhu等[47]从红树林青霉菌Penicillium janthinellum HDN13-309中发现了8个新的二氧哌嗪类生物碱Penispirozines A-H (88-95)。化合物88含有一种新型的吡嗪[1, 2]恶氮甲啉与噻吩环系统,化合物89具有6/5/6/5/6的五环结构和两个罕见的螺旋环中心。化合物90-95不仅具有螺旋-噻吩或螺旋-呋喃环体系,而且具有五环部分的手性。Zhao等[48]从海南省红树林植物根际分离到的哈茨木霉Trichoderma harzianum D13显示出较强的抗真菌植物病原体活性;进一步从其发酵产物中分离得到一个新的二酮哌嗪衍生物Trichodermamide G (96),与同源化合物相比,化合物96具有独特的含硫桥的环状体系,但其没有显著的抗植物致病真菌活性。Li等[49]从广西红树林根际土壤来源花斑曲霉真菌Apergillus verisicolor HDN11-84中发现了一种新的吡嗪嘧啶类生物碱Pyrasplorine A (97)及其新的同系物Pyrasplorines B (98)和C (100)。Pyrasplorines B (98)在温和条件下可以转化为Deg-Pyrasplorine B (99);Pyrasplorine A (97)是吡嗪嘧啶类生物碱中第一个含有螺环戊烷的化合物,其螺环戊烷部分在萜类中很常见,但在生物碱和双酮哌嗪中很少见。使用HeLa、HL-60、A549和HCT116细胞株对化合物97-100进行细胞毒性评估,结果表明所有化合物均未显示出活性[49]; Deg-Pyrasplorine B具有抗甲型H1N1流感病毒的活性,IC50为50 μmol/L[49],这类化合物往往具有较好的抗肿瘤活性,为潜在的抗癌先导化合物。Jiang等[50]从湛江红树林的木榄Bruguiera gymnorhiza中分离到一株青霉菌Penicillium sp. GD6,并从这株菌中分离得到3种新的二酮哌嗪生物碱5S-hydroxynorvaline-S-Ile (101),3S-hydroxylcyclo (S-Pro-S-Phe) (102) 和Cyclo (S-Phe-S-Gln) (103)。化合物76-103的结构如图 5所示。

|
| 图 5 化合物76-103的结构 Fig.5 Structures of compounds 76-103 |
6 其他类生物碱
除了一些常见的生物碱前体来源,有些生物碱化合物前体不明确或者前体相对小众,将这些生物碱归为其他类生物碱。Gou等[51]从红树林木榄根际土壤中分离得到一株曲霉属真菌Aspergillus sp.DM94,并从该真菌的发酵产物中获得一个吡喃酮类化合物(104),其对幽门螺杆菌Helicobacter pylori没有明显的抑制活性,MIC值>32 μg/mL。Zhou等[52]从海南三亚白鹿公园的红树林内生腐皮镰孢菌Fusarium solani HDN15-410中分离得到4个褐藻酸衍生物Fusaricates H-K (105-108),是与二元醇单元相连的褐藻酸衍生物的4种异构体(105-108)。Chokpaiboon等[53]从泰国的一种水椰Nypa fruticans内生真菌Astrosphaeriella nypae BCC 5335中分离得到一种新的生物碱Astronyurea (109)。Zhang等[22]从青霉菌Penicillium oxalicum EN-201中分离鉴定出一种新的十碳烯类似物18-Hydroxydecaturin B (110),化合物110具有天然产物中罕见的吡啶基-a-吡喃亚结构,并表现出较强的卤虫致死活性,LD50值为2.3 mmol/L。Ding等[54]从红树林黄槿Talipariti tiliaceum根际土壤青霉菌Penicillium sp.DM815的乙酸乙酯提取物中提取到一种新的山梨醇类化合物(111),利用培养的巨噬细胞RAW264.7评估了此种山梨醇类化合物的抗炎作用,实验数据显示该化合物可显著抑制LPS诱导的转录因子NFKB磷酸化。Cui等[28]从一株红树林内生菜豆间座壳菌Diaporthe phaseolorum SKS019分离得到两种新的异吲哚啉酮Meyeroguillines C和D (112和113),这些化合物是首次从该属植物的内生真菌中分离得到的生物碱。Cao等[37]从海南省东寨港红树林根际土壤来源枝孢属真菌Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1中分离得到一种新的生物碱Cladoslide C (114),将化合物114对HeLa、BEL-7402、K562和SGC-7901细胞株的细胞毒性和α-糖苷酶抑制活性进行测试,结果显示该化合物没有明显的细胞毒性和α-糖苷酶抑制活性。Hou等[55]从海南省东寨港红树林沉积物中分离得到青霉菌Penicillium brefeldium ABC190807,从该菌的乙酸乙酯提取物中分离得到1个新的嘌呤类固醇(115),该化合物对埃及伊蚊3龄幼虫无显著的杀幼虫活性,IC50值为0.089 mg/mL。Yang等[56]从一株海南岛红树林青霉菌Penicillium janthinellum HDN13-309中分离到一种新的类木霉胺生物碱N-Me-trichodermamide B (116),这种新生物碱对H2O2诱导的氧化损伤细胞具有保护作用。虽然这些生物碱的生物合成途径目前仍未明确,但是化合物结构复杂,具有良好的研究价值。化合物104-116的结构如图 6所示。
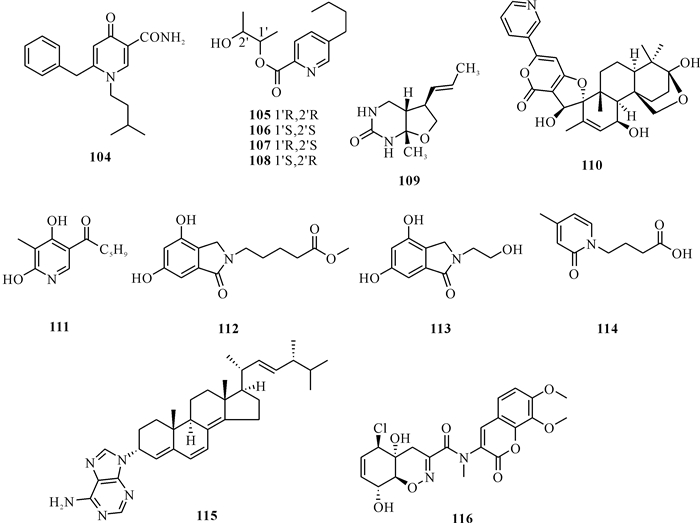
|
| 图 6 化合物104-116的结构 Fig.6 Structures of compounds 104-116 |
7 展望
综上,近几年从红树林来源真菌中发现的生物碱类化合物数量逐年增多,较多的结构类型主要集中在鸟氨酸系、色氨酸系、苯丙氨酸系、邻氨基苯甲酸系、二酮哌嗪类生物碱。其中,鸟氨酸系、色氨酸系、二酮哌嗪类生物碱不仅具有独特和复杂的化学结构,而且部分化合物还表现出较强的抗肿瘤、抗病毒、抗菌和抗炎等多种生理活性(表 1),具有潜在的研究和应用价值。
| 化合物编号 Compound number |
来源菌株 Source strain |
生物活性 Bioactivity |
参考文献 Reference |
| 1, 2 | Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1 | Cytotoxicity | [8] |
| 3 | Aspergillus versicolor SYSU-SKS025 | α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | [9] |
| 4 | Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ001 | Antibacterial activity | [10] |
| 5 | Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112 | Lipid-lowering effect | [11] |
| 8 | Talaromyces sp.HZ-YX1 | Inhibitor of Mtb PknG | [13] |
| 9 | Co-culture of strains K38 and E33 (species not identified) | Antifungal activity | [14] |
| 11 | Eutypella scoparia 1-15 | Cytotoxicity | [15] |
| 12 | Penicillium brocae MA-231 | Broad-spectrum inhibitory activity against human, aquatic and plant pathogens | [16] |
| 15-17 | Co-culture of Aspergillus versicolor IMB17-055 and Aspergillus chevalieri IMB18-208 | Antifungal activity | [19] |
| 28 | Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-84 | Cytotoxicity | [24] |
| 31, 32 | Neosartorya udagawae HDN13-313 | Anti-influenza A (H1N1) virus activity | [26] |
| 36 | Penicillium brocae MA-231 | Cytotoxicity,antibacterial activity | [27] |
| 38-40 | Penicillium brocae MA-231 | Antibacterial activity | [28] |
| 42, 43 | Penicillium oxalicum EN-201 | Brine shrimp lethal activity | [29] |
| 56 | Aspergillus versicolor HDN11-84 | Anti-influenza A (H1N1) virus activity | [33] |
| 58 | Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025 | α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | [34] |
| 64 | Penicillium sp.DM815 | Anti-inflammatory action | [35] |
| 65 | Penicillium sp.IMB17-046 | Broad-spectrum antiviral activity and antibacterial activity | [36] |
| 66, 67 | Penicillium raistrickii IMB17-034 | Anti-hepatitis C virus activity | [37] |
| 68 | Eupenicillium sp.HJ002 | Cytotoxicity | [38] |
| 77 | Diaporthe sp.SYSUHQ3 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase B inhibitory activity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis | [41] |
| 80 | Penicillium chrysogenum V11 | Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity | [42] |
| 81, 82, 85 | Mucor irregularis QEN-189 | Cancer cell inhibitory activity | [43] |
| 87, 88 | Penicillium chrysogenum V11 | Compound 87 has cytotoxic activity and compound 88 has antibacterial activity | [44] |
| 89 | Aspergillus taichungensis ZHN-7-07 | Cytotoxicity | [45] |
| 94, 96 | Eurotium rubrum MA-150 | Lethal activity of brine shrimp | [47] |
| 102-105 | Penicillium herquei JX4 | Broad-spectrum antifungal activity | [52] |
| 110 | Penicillium janthinellum HDN13-309 | It has a protective effect on H2O2-induced oxidative damage in cells | [53] |
| 113, 114 | Phomopsis sp.33 | Compound 113, 114 had inhibitory activity on nitric oxide,and compound 114 has good scavenging ability for DPPH free radical | [54] |
红树林作为一种特殊的植物群落,其独特的环境孕育了丰富的微生物资源。红树林来源真菌的次级代谢产物中存在一系列结构新颖、活性良好的生物活性化合物,为新型海洋药物的开发提供了丰富的化学结构本体。海洋土壤含有的多种多样的化学元素为红树林内生真菌的代谢产物提供了更多的可能性,开发潜力巨大,但研究依然面临着一些问题:(1)化合物的发现随机性较大,基于色谱学和波普学特征、有目的地追踪分离的研究较少;(2)化合物的化学合成研究较多,但生物合成研究,尤其是从基因功能分析和开发角度开展的研究较少;(3)化合物活性多集中在细胞毒和抗菌研究方面,活性功能评价相对单一,尤其是与环境相关的化学生态功能研究较少;(4)化合物来源多集中在有限的几个菌属和环境上,应在重点关注其资源分布特征的基础上,进一步拓展资源发现的范围。随着海洋科技的进步和研究的不断深入,如果能加强结构改造和活性机制研究,红树林来源真菌含量丰富、结构特殊的代谢产物必将在药物先导的发现中贡献出更多的力量。
| [1] |
徐静. 红树林微生物天然产物化学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 6-7.
|
| [2] |
高剑, 李赤, 王燕, 等. 红树林内生真菌多样性及其应用潜能[J]. 菌物研究, 2013, 11(3): 212-216. |
| [3] |
邓祖军, 曹理想, 周世宁. 红树林内生真菌的分离及代谢产物生物活性的初步研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 49(2): 100-104. |
| [4] |
周婧, 杨琦, 李钢, 等. 红树属植物内生真菌多样性及其代谢产物研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(1): 89-102. |
| [5] |
宋双, 薛艳钰, 陆勇军, 等. 南海红树林内生真菌Fusarium solani 387#次级代谢产物研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 54(5): 67-71. |
| [6] |
刘爱荣, 吴晓鹏, 徐同. 红树林内生真菌研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(4): 912-918. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2007.04.034 |
| [7] |
王成, 张国建, 刘文典, 等. 海洋药物研究开发进展[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2019, 38(6): 35-69. |
| [8] |
WANG P, CUI Y, CAI C H, et al. Two new succinimide derivatives cladosporitins A and B from the mangrove-derived fungus Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1[J]. Marine Drugs, 2018, 17(1): 4. DOI:10.3390/md17010004 |
| [9] |
CUI H, LIU Y N, LI T M, et al. 3-Arylisoindolinone and sesquiterpene derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungi Aspergillus versicolor SYSU-SKS025[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 124: 177-181. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2017.11.006 |
| [10] |
YANG L J, LIAO H X, BAI M, et al. One new cytochalasin metabolite isolated from a mangrove-derived fungus Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ001[J]. Natural Product Research, 2018, 32(2): 208-213. DOI:10.1080/14786419.2017.1346641 |
| [11] |
GUO W Q, WANG S, LI N, et al. Saroclides A and B, cyclic depsipeptides from the mangrove-derived fungus Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2018, 81(4): 1050-1054. DOI:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00644 |
| [12] |
WANG P, CUI Y, CAI C H, et al. A new cytochalasin derivative from the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Xylaria sp.HNWSW-2[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, 2018, 20(10): 1002-1007. DOI:10.1080/10286020.2018.1497610 |
| [13] |
CHEN S H, HE L Q, CHEN D N, et al. Talaramide A, an unusual alkaloid from the mangrove endophytic fungus Talaromyces sp.(HZ-YX1) as an inhibitor of mycobacterial PknG[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 41(11): 4273-4276. DOI:10.1039/C7NJ00059F |
| [14] |
DING W J, LU Y C, FENG Z H, et al. A new nonadride derivative from the co-culture broth of two mangrove fungi[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2017, 53(4): 691-693. DOI:10.1007/s10600-017-2092-2 |
| [15] |
QI S, WANG Y, ZHENG Z H, et al. Cytochalasans and sesquiterpenes from Eutypella scoparia 1-15[J]. Natural Product Communications, 2015, 10(12): 2027-2030. |
| [16] |
MENG L H, LI X M, LIU Y, et al. Polyoxygenated dihydropyrano[2, 3-c]pyrrole-4, 5-dione derivatives from the marine mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium brocae MA-231 and their antimicrobial activity[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2015, 26(5): 610-612. DOI:10.1016/j.cclet.2015.01.024 |
| [17] |
ZHOU Z F, KURTÁN T, YANG X H, et al. Penibruguieramine A, a novel pyrrolizidine alkaloid from the endophytic fungus Penicillium sp.GD6 associated with chinese mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza[J]. Organic Letters, 2014, 16(5): 1390-1393. DOI:10.1021/ol5001523 |
| [18] |
WANG X Y, YE X S, GAO S, et al. Cytotoxic compound triacremoniate from marine fungus Acremonium citrinum. MMF4[J]. Fitoterapia, 2020, 147: 104766. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104766 |
| [19] |
LI J, CHEN M H, HAO X M, et al. Structural revision and absolute configuration of burnettramic acid A[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(1): 98-101. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b04008 |
| [20] |
ZHANG H M, JU C X, LI G, et al. Dimeric 1, 4-benzoquinone derivatives with cytotoxic activities from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp.L129[J]. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17(7): 383-383. DOI:10.3390/md17070383 |
| [21] |
YU G H, ZHOU G L, ZHU M L, et al. Neosartoryadins A and B, fumiquinazoline alkaloids from a mangrove-derived fungus Neosartorya udagawae HDN13-313[J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(2): 244-247. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02964 |
| [22] |
ZHANG P, LI X M, LIU H, et al. Two new alkaloids from Penicillium oxalicum EN-201, an endophytic fungus derived from the marine mangrove plant Rhizophora stylosa[J]. Phytochemistry Letters, 2015, 13: 160-164. DOI:10.1016/j.phytol.2015.06.009 |
| [23] |
ZHENG Y Y, SHEN N X, LIANG Z Y, et al. Paraherquamide J, a new prenylated indole alkaloid from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium janthinellum HK1-6[J]. Natural Product Research, 2020, 34(3): 378-384. DOI:10.1080/14786419.2018.1534105 |
| [24] |
LI J, WANG Y J, HAO X M, et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral natural products from the marine-derived Penicillium sp.IMB17-046[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(15): 2821. DOI:10.3390/molecules24152821 |
| [25] |
LI J, HU Y Y, HAO X M, et al. Raistrickindole A, an anti-hcv oxazinoindole alkaloid from Penicillium raistrickii IMB17-034[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2019, 82(5): 1391-1395. DOI:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00259 |
| [26] |
ZHENG C J, BAI M, ZHOU X M, et al. Penicilindoles A-C, cytotoxic indole diterpenes from the mangrove-derived fungus Eupenicillium sp.HJ002[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2018, 81(4): 1045-1049. DOI:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00673 |
| [27] |
YANG B, TAO H M, LIN X P, et al. Prenylated indole alkaloids and chromone derivatives from the fungus Penicillium sp.SCSIO041218[J]. Tetrahedron, 2018, 74(1): 77-82. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2017.11.038 |
| [28] |
CUI H, YU J C, CHEN S H, et al. Alkaloids from the mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe phaseolorum SKS019[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2017, 27(4): 803-807. |
| [29] |
CUI H, LIN Y, LUO M C, et al. Diaporisoindoles A-C: three isoprenylisoindole alkaloid derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp.SYSU-HQ3[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(20): 5621-5624. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b02748 |
| [30] |
ZHU X W, ZHOU D L, LIANG F Y, et al. Penochalasin K, a new unusual chaetoglobosin from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum V11 and its effective semi-synthesis[J]. Fitoterapia, 2017, 123: 23-28. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2017.09.016 |
| [31] |
GAO S S, LI X M, WILLIAMS K, et al. Rhizovarins A-F, indole-diterpenes from the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Mucor irregularis QEN-189[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2016, 79(8): 2066-2074. DOI:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00403 |
| [32] |
HUANG S, CHEN H Y, LI W S, et al. Bioactive chaetoglobosins from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum[J]. Marine Drugs, 2016, 14(10): 172. DOI:10.3390/md14100172 |
| [33] |
CAI S X, SUN S W, PENG J X, et al. Okaramines S-U, three new indole diketopiperazine alkaloids from Aspergillus taichungensis ZHN-7-07[J]. Tetrahedron, 2015, 71(22): 3715-3719. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2014.09.019 |
| [34] |
CHEN S H, LIU Z M, LIU Y Y, et al. New depsidones and isoindolinones from the mangrove endophytic fungus Meyerozyma guilliermondii (HZ-Y2) isolated from the South China Sea[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2015, 11: 1187-1193. DOI:10.3762/bjoc.11.133 |
| [35] |
MENG L H, DU F Y, LI X M, et al. Rubrumazines A-C, indolediketopiperazines of the isoechinulin class from Eurotium rubrum MA-150, a fungus obtained from marine mangrove-derived rhizospheric soil[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2015, 78(4): 909-913. DOI:10.1021/np5007839 |
| [36] |
LV H W, WANG K B, XUE Y X, et al. Three new metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp.WHUF03110[J]. Natural Product Communications, 2021, 16(10): 1934578X2110550. |
| [37] |
CAO X, GUO L, CAI C H, et al. Metabolites from the mangrove-derived fungus Cladosporium sp.HNWSW-1[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 773703. DOI:10.3389/fchem.2021.773703 |
| [38] |
CHEN C M, CHEN W H, TAO H M, et al. Diversified polyketides and nitrogenous compounds from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 39(8): 2132-2140. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.202100226 |
| [39] |
CHEN H P, HUANG M X, LI X W, et al. Phochrodines A-D, first naturally occurring new chromenopyridines from mangrove entophytic fungus Phomopsis sp.33#[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 124: 103-107. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2017.10.013 |
| [40] |
ZHENG C J, WU L Y, LI X B, et al. Structure and absolute configuration of aspergilumamide A, a novel lumazine peptide from the mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus sp.[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2015, 98(3): 368-373. DOI:10.1002/hlca.201400197 |
| [41] |
LI J, ZHONG Y S, YUAN J, et al. A new terminal cyano group-containing benzodiazepine alkaloid from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium sp.[J]. Natural Product Communications, 2015, 10(9): 1549-1551. |
| [42] |
ZHOU X M, ZHENG C J, SONG X M, et al. Bioactive acetaminophen derivatives from Penicillum herquei JX4[J]. Fitoterapia, 2019, 139: 104400. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104400 |
| [43] |
CHEN C M, CHEN W H, PANG X Y, et al. Pyrrolyl 4-quinolone alkaloids from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025:chiral resolution, configurational assignment, and enzyme inhibitory activities[J]. Phytochemistry, 2021, 186: 112730. DOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112730 |
| [44] |
LI F, GUO W Q, WU L, et al. Saroclazines A-C, thio-diketopiperazines from mangrove-derived fungi Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-84[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2018, 41(1): 30-34. DOI:10.1007/s12272-017-0961-7 |
| [45] |
MENG L H, WANG C Y, MÁNDI A, et al. Three diketopiperazine alkaloids with spirocyclic skeletons and one bisthiodiketopiperazine derivative from the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium brocae MA-231[J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(20): 5304-5307. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02620 |
| [46] |
MENG L H, ZHANG P, LI X M, et al. Penicibrocazines A-E, five new sulfide diketopiperazines from the marine-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium brocae[J]. Marine Drugs, 2015, 13(1): 276-287. DOI:10.3390/md13010276 |
| [47] |
ZHU M L, YANG Z, WANG H T, et al. Penispirozines A-H, three classes of dioxopiperazine alkaloids with spirocyclic skeletons isolated from the mangrove-derived Penicillium janthinellum[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(9): 2647-2654. DOI:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00451 |
| [48] |
ZHAO D L, ZHANG X F, HUANG R H, et al. Antifungal nafuredin and epithiodiketopiperazine derivatives from the mangrove-derived fungus Trichoderma harzianum D13[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1495. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01495 |
| [49] |
LI F, SUN C X, CHE Q, et al. Pyrazinopyrimidine alkaloids from a mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor HDN11-84[J]. Phytochemistry, 2021, 188: 112817. DOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112817 |
| [50] |
JIANG C S, ZHOU Z F, YANG X H, et al. Antibacterial sorbicillin and diketopiperazines from the endogenous fungus Penicillium sp.GD6 associated Chinese mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 2018, 16(5): 358-365. DOI:10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30068-2 |
| [51] |
GOU X S, JIA J, XUE Y X, et al. New pyrones and their analogs from the marine mangrove-derived Aspergillus sp.DM94 with antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(18): 7971-7978. DOI:10.1007/s00253-020-10792-9 |
| [52] |
ZHOU G L, QIAO L, ZHANG X M, et al. Fusaricates H-K and fusolanones A-B from a mangrove endophytic fungus Fusarium solani HDN15-410[J]. Phytochemistry, 2019, 158: 13-19. DOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.10.035 |
| [53] |
CHOKPAIBOON S, UNAGUL P, KONGTHONG S, et al. A pyrone, naphthoquinone, and cyclic urea from the marine-derived fungus Astrosphaeriella nypae BCC 5335[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2016, 57(10): 1171-1173. DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.02.002 |
| [54] |
DING W J, WANG F F, LI Q W, et al. Isolation and characterization of anti-inflammatory sorbicillinoids from the mangrove-derived fungus Penicillium sp.DM815[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2021, 18(7): e2100229. |
| [55] |
HOU Z M, YU S Q, TAO M, et al. New purinyl-steroid and other constituents from the marine fungus Penicillium brefeldianum ABC190807:larvicidal activities against Aedes aegypti[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 2021: 1-6. |
| [56] |
YANG Z, ZHU M L, LI D H, et al. N-Me-trichodermamide B isolated from Penicillium janthinellum, with antioxidant properties through Nrf2-mediated signaling pathway[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2017, 25(24): 6614-6622. |



