2. 广西壮族自治区海洋研究所, 广西海洋生物技术重点实验室, 广西北海 536000;
3. 河南师范大学生命科学学院, 河南新乡 453007;
4. 广西壮族自治区水产科学研究院, 广西水产遗传育种与健康养殖重点实验室, 广西南宁 530021;
5. 广西民族大学海洋与生物技术学院, 广西南宁 530006;
6. 广西海洋天然产物与组合生物合成化学重点实验室, 广西南宁 530007
2. Guangxi Key Laboratory for Marine Biotechnology, Guangxi Institute of Oceanography, Beihai, Guangxi, 536000, China;
3. College of Life Science, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, Henan, 453007, China;
4. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Aquatic Genetic Breeding and Healthy Breeding, Guangxi Academy of Fishery Science, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China;
5. School of Marine Sciences and Biotechnology, Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning, Guangxi, 530006, China;
6. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Marine Natural Products and Combinatorial Biosynthesis Chemistry, Nanning, Guangxi, 530007, China
广西是我国的水产养殖大省,主要养殖品种包括卵形鲳鲹、石斑鱼、草鱼、斑点叉尾鮰、罗非鱼、对虾和贝类等。近年来,随着市场需求量的不断增加,广西水产养殖业进入快速发展期,养殖规模不断扩大,养殖效益持续增加[1-2]。其中,卵形鲳鲹肉质细腻,营养丰富,目前国内卵形鲳鲹年产量则超过10万吨,养殖效益极为显著。然而在高密度养殖条件下,各种病害频发暴发,造成了巨大经济损失[3-4]。广西水产疫病防控研究工作比较滞后,针对主要水产养殖品种,既缺少详细系统的流行病学调查,更缺少高效的防控功能产品,这些不利因素影响了广西水产养殖业的健康可持续发展。2017年夏季,养殖于广西钦州湾海域的近海网箱中的卵形鲳鲹暴发了溶藻弧菌病,给当地卵形鲳鲹养殖业造成了巨大的经济损失[4]。据华南地区的研究报道,溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus)是严重危害包括广西北部湾海域在内的华南沿海地区海水养殖鱼类的主要条件致病菌之一,其导致的鱼病具有发病速度快、累计死亡率高、流行范围广的特点[5-6]。目前溶藻弧菌的检测方法主要包括菌落形态观察结合生理生化反应指标的生物学检验,以及基于细菌16S DNA基因测序的分子生物学检测技术等[7]。这些方法虽然能够实现对溶藻弧菌病的检测诊断,但是却存在技术操作繁琐、仪器试剂昂贵、检测耗时长等诸多不足,因此仅适用于实验室条件下少量样品检测。为满足养殖现场对溶藻弧菌病快速准确检测的要求,本研究利用先前筛选获得的特异性识别溶藻弧菌活菌的核酸适配体VA8[8],开发出一种能够快速检测溶藻弧菌的新型的核酸适配体吸附检测技术(VA8-based enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay, VA8-ELASA),并对VA8-ELASA技术检测溶藻弧菌的特异性和灵敏性进行了分析研究。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料本实验中所使用的溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus)从广西钦州湾网箱养殖的发病卵形鲳鲹中分离得到,保存于本实验室,编号为TOQZ01[4];哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)从北海铁山港网箱养殖的发病卵形鲳鲹中分离得到,编号为BHVH01;嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)从广西南宁池塘养殖的发病草鱼中分离获得。TMB显色液购自碧云天生物技术公司,链霉素标记的HRP(Streptavidin-HRP)购自Thermo公司;生物素标记的核酸适配体VA8(Biotin-VA8)和生物素标记的非特异性单链核酸文库(Biotin-ssDNA Library)由上海生工合成;本实验使用的仪器包括多功能酶标仪,无菌操作台,Nikon倒置显微镜,Nikon激光共聚焦显微镜,Thermo PCR仪,生化培养箱,常温低速离心机,低温高速离心机,水浴锅。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 VA8-ELASA操作流程VA8-ELASA的操作方法参考先前的报道,并进行了优化改进[9-10]。具体步骤是:将生物素(Biotin)标记的核酸适配体VA8(Biotin-VA8)在92℃高温水浴变性10 min,然后迅速插入到冰中复性10 min;将Biotin-VA8 (300 nmol/L)与待测菌液在冰上结合20 min,然后用PBS 1 000 g离心清洗3次,移除上清,将沉淀的样品与200 μL Streptavidin-HRP(1:10 000)混匀结合20 min;用磷酸缓冲盐溶液PBS 1 000 g离心清洗5次后,将样品与200 μL TMB显色液混匀,避光反应15 min,加入50 μL H2SO4(2 mol/L)终止反应;使用多功能酶标仪读取待测样品在450 nm处的吸光值并记录结果。每个反应均做3个重复。
1.2.2 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的特异性分析将生物素(Biotin)标记的核酸适配体VA8 (Biotin-VA8, 300 nmol/L)经过92℃恒温水浴、冰浴处理;试验组(Test 1)为Biotin-VA8 (300 nmol/L)与1 mL溶藻弧菌菌液(1×108 CFU/mL)孵育结合,对照组设置3组:对照组1(Control 1),Biotin-VA8 (300 nmol/L)与1 mL哈维氏弧菌菌液(1×108 CFU/mL)孵育结合;对照组2(Control 2),Biotin-VA8(300 nmol/L)与1 mL嗜水气单胞菌菌液(1×108 CFU/mL)孵育结合;对照组3(Control 3),Biotin-ssDNA Library与1 mL溶藻弧菌菌液(1×108 CFU/mL)孵育结合;对照组4(Control 4),未作任何处理的1 mL溶藻弧菌菌液(1×108 CFU/mL)。孵育结合完成后,将各组样品用PBS离心清洗3次,然后富集到的样品与200 μL Streptavidin-HRP(1:10 000)混匀结合20 min。后续的显色反应与检测步骤参看1.2.1小节。每个反应均做3个重复。
1.2.3 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的数量灵敏性分析将溶藻弧菌稀释至不同的浓度:5×107 CFU/mL, 5×106 CFU/mL, 5×105 CFU/mL, 1×105 CFU/mL, 5×104 CFU/mL, 1×104 CFU/mL, 5×103 CFU/mL, 1×103 CFU/mL。试验组(Test)是取1 mL不同浓度的菌液用PBS 1 000 g离心清洗3次,然后与Biotin-VA8在冰上结合30 min。Biotin-ssDNA Library与相应浓度的溶藻弧菌的孵育实验作为对照组(Control)。后续具体的检测操作参看1.2.1小节。每个反应均做3个重复。
1.2.4 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的时间灵敏性分析我们随后对VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的孵育时长灵敏性进行了分析。试验组(Test)是取1 mL溶藻弧菌TOQZ01(1×108 CFU/mL)用PBS 1 000 g离心清洗3次,然后与Biotin-VA8在冰上分别孵育结合60 min,30 min,20 min,10 min,5 min和1 min。Biotin-ssDNA Library与1 mL溶藻弧菌(1×108 CFU/mL)孵育相应时长的实验作为对照组(Control)。后续具体的检测操作参看1.2.1小节。每个反应均做3个重复。
2 结果与分析 2.1 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的特异性高在先前研究中,基于前沿的指数富集的配基系统进化技术(SELEX)筛选获得特异性识别溶藻弧菌活菌的核酸适配体VA8,VA8的核苷酸序列如表 1所示。VA8-ELASA的操作流程如图 1所示。使用VA8-ELASA技术对溶藻弧菌进行检测发现,与4个对照组相比,VA8-ELASA能够特异性地检测溶藻弧菌,而对非靶标细菌没有明显的识别作用。由此证明,VA8-ELASA能够用于卵形鲳鲹养殖中溶藻弧菌病的特异性检测与诊断(图 2)。
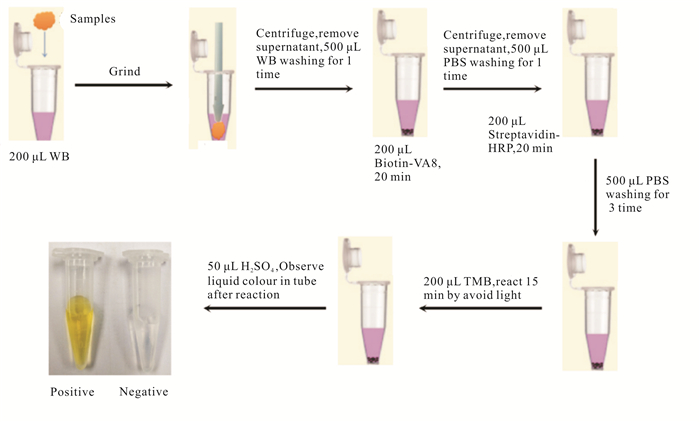
|
| 图 1 VA8-ELASA操作示意图 Fig.1 Graphic procedure of VA8-ELASA |

|
| **P < 0.01差异极显著 **P < 0.01 was considered extremely different 图 2 VA8-ELASA特异性检测溶藻弧菌结果 Fig.2 The results of VA8-ELASA specific detection of V.alginolyticus |
| 核酸适配体 Aptamer |
核苷酸序列 Nucleotide Sequences |
| VA8 | 5′-GACGCTTACTCAGGTGTGACTCGCGTTTT ATTGGTGTGGGGCTGGGGCGGTGGGTGGCT CTACTGGTTCCGTTCGAAGGACGCAGATGA AGTCTC-3′ |
2.2 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的数量灵敏性高
使用VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌时,对照组中各组的吸光值均没有明显差异,实验组中溶藻弧菌的数量越多,在450 nm处的吸光值就越高,即VA8-ELASA是以浓度梯度依赖的方式检测溶藻弧菌TOQZ01。当溶藻弧菌的数目低至5×104 CFU/mL时,VA8-ELASA仍可灵敏地检测到溶藻弧菌(图 3)。
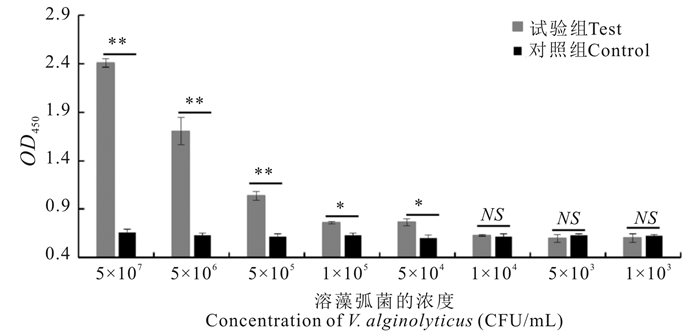
|
| *P < 0.05差异显著, **P < 0.01差异极显著,NS无显著性差异 *P < 0.05 was considered significantly different, **P < 0.01 was considered extremely different, NS was considered no significant difference 图 3 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌细胞的数量灵敏性 Fig.3 The quantity sensitivity of VA8-ELASA for detection of V.alginolyticus cells |
2.3 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌的时间灵敏性高
使用VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌时,与对照组中不同孵育结合时间条件下的吸光值均没有明显差异的结果相比,孵育结合时间越长,实验组中待测样品在450 nm处的吸光值就越高,即VA8-ELASA以孵育结合时长依赖的方式检测溶藻弧菌TOQZ01。当孵育结合时长短至1 min时,VA8-ELASA仍可灵敏地检测到溶藻弧菌(图 4)。因此,VA8-ELASA可以用于溶藻弧菌的快速检测诊断。
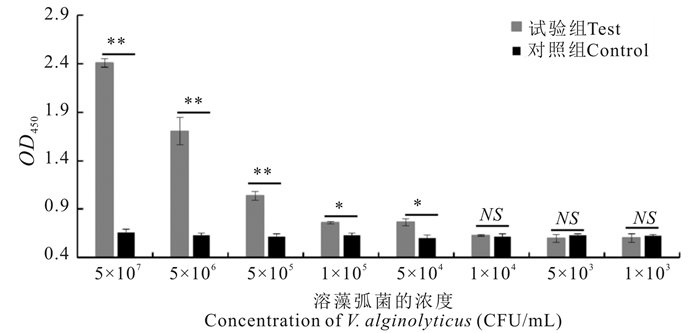
|
| *P < 0.05差异显著, **P < 0.01差异极显著,NS无显著性差异 *P < 0.05 was considered significantly different, **P < 0.01 was considered extremely different, NS was considered no significant difference 图 4 VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌细胞的时间灵敏性 Fig.4 The time sensitivity of VA8-ELASA for V.alginolyticus cells |
3 讨论
近年来,水产养殖中细菌性和病毒性疾病频发暴发,严重影响着水生生态稳定以及水产养殖业的健康可持续发展。其中,溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus)是一种条件致病菌,能够感染鱼、虾、蟹、贝等众多海水养殖品种[7, 11]。溶藻弧菌通常在夏季水温高、环境恶化时以及养殖动物免疫力下降时暴发流行,通过在在感染和快速增殖过程中向胞外释放细胞毒素等代谢产物来干扰并破坏养殖动物的正常新陈代谢,进而造成严重的细胞损伤和出血性溃疡、内脏器官肿大等组织病变,最终导致动物死亡[5, 7, 12]。溶藻弧菌引起的细菌病具有发病迅速、死亡率高、流行面广等特点,给广西等华南沿海地区海水养殖业造成了巨大的损失。为实现广西卵形鲳鲹养殖中溶藻弧菌病的快速诊断、实时监控和有效预防的目的,本研究中我们利用前沿的核酸适配体技术,着力开发用于溶藻弧菌快速检测的核酸适配体吸附检测技术。
核酸适配体是利用指数富集的配基系统进化技术(System evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment, SELEX)筛选最终获得能够特异性识别靶物质的单链寡核苷酸[13]。核酸适配体具有易筛选获得、合成成本低、易修饰、稳定性强、批次间质量相同、识别结合靶物质的特异性高等诸多优点。作为一种新型的分子探针,核酸适配体在分析检测、临床诊断、新药研发等领域具有广阔的应用前景[14]。目前,核酸适配体在水生生物病原研究领域也已取得了较快进展。据报道,已成功筛选获得高特异性核酸适配体的水产病害包括新加坡石斑鱼虹彩病毒(Singapore grouper iridovirus)[15-16],赤点石斑鱼神经坏死症病毒(Red spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus)[17],卵形鲳鲹源神经坏死病毒(Trachinotus ovatus NNV)[18],鲤春病毒血症病毒(Spring viremia of carp virus)[19],牙鲆弹状病毒(Hirame rhabdovirus virus)[20],病毒性出血性败血症病毒(Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus)[21],中华鳖虹彩病毒(Soft-shelled turtle iridovirus)[22],溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus)[8, 23],哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)[24],嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)[25]和鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium)[26]等。基于这些核酸适配体建立了多种新型检测技术中,包括核酸适配体免疫吸附测定技术(Enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay,ELASA)[9-10],核酸适配体-纳米金检测技术等[27]和核酸适配体-荧光分子检测探针检测技术[28]等。例如,Zhou等[10]利用特异性结合赤点石斑鱼神经坏死症病毒CP衣壳蛋白的核酸适配体A10,研发出的sandwich ELASA技术,在病毒感染的细胞数目低至4 000个,以及孵育时间短至10 min时,sandwich ELASA技术均能检测到赤点石斑鱼神经坏死症病毒的感染,并且sandwich ELASA技术检测RGNNV感染的灵敏度与PCR技术相当,ELASA技术操作简便快捷、稳定性强。
本研究中,我们基于特异性识别溶藻弧菌活菌的核酸适配体VA8开发出一种新型的核酸适配体吸附检测技术(VA8-ELASA)用于溶藻弧菌的快速检测。当溶藻弧菌TOQZ01的浓度低至5×104 CFU/mL,VA8-ELASA中Biotin-VA8与溶藻弧菌TOQZ01孵育结合时长短至1 min时,VA8-ELASA均能够清楚地检测到溶藻弧菌。综上,VA8-ELASA技术具有耗时短、操作便捷、灵敏性高等优点,能够用于卵形鲳鲹养殖中溶藻弧菌病的特异性检测与快速诊断。本研究成果为丰富和提高水产疫病防控领域的检测技术研究提供了新方法和新思路。
4 结论本研究开发出一种新型的核酸适配体吸附检测技术(VA8-ELASA)用于溶藻弧菌的快速检测。实验结果表明,VA8-ELASA能够用于溶藻弧菌病的特异性检测;VA8-ELASA检测溶藻弧菌具有耗时短、灵敏性高等优点;VA8-ELASA有望实现对溶藻弧菌病的快速诊断、实时监控和有效预防。
| [1] |
李鹏飞, 余庆, 覃仙玲, 等. 广西北部湾海水养殖业现状与病害防控技术体系研究展望[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(1): 15-25. |
| [2] |
李坚明. "十三五"广西水产养殖业发展战略研究[J]. 中国渔业经济, 2016, 34(4): 25-31. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-590X.2016.04.004 |
| [3] |
LI P, YU Q, LI F, et al. First identification of the nervous necrosis virus isolated from cultured golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) in Guangxi, China[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2018, 41(7): 1177-1180. DOI:10.1111/jfd.12805 |
| [4] |
余庆, 李菲, 王一兵, 等. 广西北部湾大宗海水养殖鱼类卵形鲳鲹感染溶藻弧菌及其致病性的研究[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(1): 68-73. |
| [5] |
崔婧, 范雪亭, 刘文竹, 等. 华南地区海水养殖鱼类主要弧菌病原的分离与鉴定[J]. 海南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 32(3): 244-251. |
| [6] |
夏立群, 黄郁葱, 鲁义善. 卵形鲳鲹主要病害及其研究进展[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2012, 18(23): 140-143, 150. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2012.23.065 |
| [7] |
赖迎迢, 陶家发, 孙承文, 等. 鱼源溶藻弧菌生物学特性和病理组织学观察[J]. 微生物学报, 2014, 54(11): 1378-1384. |
| [8] |
YU Q, LIU M, SU H, et al. Selection and characterization of ssDNA aptamers specifically recognizing pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2019, 42(6): 851-858. DOI:10.1111/jfd.12985 |
| [9] |
LI P, ZHOU L, WEI J, et al. Development and characterization of aptamer-based enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay for the detection of Singapore grouper iridovirus infection[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2016, 121(3): 634-643. DOI:10.1111/jam.13161 |
| [10] |
ZHOU L, LI P, NI S, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of redspotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) infection by aptamer-coat protein-aptamer sandwich enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay (ELASA)[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2017, 40(12): 1831-1838. DOI:10.1111/jfd.12656 |
| [11] |
LIU P, CHEN Y C, LEE K K. Pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from diseased small abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta[J]. Microbios, 2001, 104(408): 71-77. |
| [12] |
LIU X F, ZHANG H, LIU X, et al. Pathogenic analysis of Vibrio alginolyticus infection in a mouse model[J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2014, 59(2): 167-171. DOI:10.1007/s12223-013-0279-x |
| [13] |
ELLINGTON A D, SZOSTAK J W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands[J]. Nature, 1990, 346(6287): 818-822. DOI:10.1038/346818a0 |
| [14] |
BUNKA D H J, STOCKLEY P G. Aptamers come of age at last[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2006, 4(8): 588-596. DOI:10.1038/nrmicro1458 |
| [15] |
LI P, WEI S, ZHOU L, et al. Selection and characterization of novel DNA aptamers specifically recognized by Singapore grouper iridovirus-infected fish cells[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2015, 96(11): 3348-3359. DOI:10.1099/jgv.0.000270 |
| [16] |
LI P, YAN Y, WEI S, et al. Isolation and characterization of a new class of DNA aptamers specific binding to Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) with antiviral activities[J]. Virus Research, 2014, 188: 146-154. DOI:10.1016/j.virusres.2014.04.010 |
| [17] |
ZHOU L, LI P, YANG M, et al. Generation and characterization of novel DNA aptamers against coat protein of grouper nervous necrosis virus (GNNV) with antiviral activities and delivery potential in grouper cells[J]. Antiviral Research, 2016, 129: 104-114. DOI:10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.02.009 |
| [18] |
YU Q, LIU M, WEI S, et al. Characterization of ssDNA aptamers specifically directed against Trachinotus ovatus NNV (GTONNV)-infected cells with antiviral activities[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2019, 100(3): 380-391. DOI:10.1099/jgv.0.001226 |
| [19] |
于力, 王津津, 卢奕良, 等. 鲤春病毒血症病毒核酸适配体的筛选及分析[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2017, 34(2): 101-105. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2017.02.029 |
| [20] |
HWANG S D, MIDORIKAWA N, PUNNARAK P, et al. Inhibition of hirame rhabdovirus growth by RNA aptamers[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2012, 35(12): 927-934. DOI:10.1111/jfd.12000 |
| [21] |
PUNNARAK P, SANTOS M D, HWANG S D, et al. RNA aptamers inhibit the growth of the fish pathogen viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV)[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2012, 14(6): 752-761. DOI:10.1007/s10126-012-9448-1 |
| [22] |
LI P, ZHOU L, YU Y, et al. Characterization of DNA aptamers generated against the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus with antiviral effects[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2015, 11: 245-251. DOI:10.1186/s12917-015-0559-6 |
| [23] |
TANG X M, ZHENG J, YAN Q P, et al. Selection of aptamers against inactive Vibrio alginolyticus and application in a qualitative detection assay[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(6): 909-914. DOI:10.1007/s10529-013-1154-1 |
| [24] |
郑江, 郝聚敏, 宋林生, 等. 哈维氏弧菌适配子的SELEX筛选及其亲和特异性研究[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2014, 41(7): 704-711. |
| [25] |
李元跃, 王雷, 陈融斌, 等. SELEX筛选嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)适体方法的建立[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(2): 318-322. |
| [26] |
DUAN N, WU S, YU Y, et al. A dual-color flow cytometry protocol for the simultaneous detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and salmonella typhimurium using aptamer conjugated quantum dots as labels[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 804: 151-158. DOI:10.1016/j.aca.2013.09.047 |
| [27] |
HUANG Y F, LIN Y W, LIN Z H, et al. Aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer cells through light scattering[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2010, 11(4): 775-783. |
| [28] |
李鹏飞, 余庆, 李菲, 等. 新型核酸适配体-荧光分子检测探针用于石斑鱼虹彩病病毒病的快速诊断[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(1): 63-67. |



