【研究意义】 微生物是宿主自身和生长环境中存在的一种分解代谢类群,在机体健康生长过程中起关键性作用,是当今研究领域中不可或缺的部分[1-2]。对于养殖动物机体而言,肠道是微生物寄生的场所,细菌通过特定的方式黏附在肠黏膜上,肠道内的理化性质和营养物质的种类客观决定所黏附共生肠道微生物的结构和功能,调控着机体自身的代谢系统及免疫系统。研究表明,生态环境的差异化,不仅可以满足宿主对营养免疫的需求,又能使细菌菌群优势种在结构组成上既有共性又存在着明显的差异,最终实现应用效果[3-5]。不同养殖方式下,养殖水体以及养殖动物肠道中微生物有所不同,从而表现出多样性。微生物的多样性不仅包括所有的生命形式、生态系统和过程,还包括有关微生物在遗传、分类和生态系统水平上的联系[6-7]。因此,从微生物多样性角度探讨分析不同养殖系统的作用具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】在实际养殖过程中,外界因素会从不同方面对养殖动物健康、养殖效益等产生负面影响,如水体中非离子氨、亚硝酸氮等浓度较高时,养殖动物活力会下降且生长缓慢,甚至死亡[8-9];投喂大量饵料时,仅有约30%被养殖对象所利用,剩余70%则以残饵、粪便等形式落入养殖环境中,从而影响养殖水体质量、微生物菌群结构以及生态代谢系统等。近年来,循环水养殖系统以众多优点被水产养殖业所认可。Davidson等[10]采用循环水养殖系统探究其对虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)生长的影响;Drengstig等[11]在循环水养殖系统中试验欧洲龙虾(Homarus gammarus L.)的生长响应,同样产生了较好的效果;谭建等[12]研究证实循环水养殖凡纳滨对虾具有各种优势。宏基因组测序,是对特定环境(或者特定生境)样品中所有的微生物基因组序列进行高通量测定,用以分析微生物群体的基因组成及功能,解读微生物群体的多样性与丰度,探求微生物与环境、宿主之间的关系,发掘和研究新的以及特定功能基因。相对于传统的生态学方法来说,该技术目前应用较多,且能更灵敏、准确地反映出样品中细菌群落的真实情况[13-15]。如薛明等[14]通过高通量测序技术研究分析凡纳滨对虾育苗期水体菌群结构特征,讨论微生物菌群在病害防控及维持健康养殖稳态中的重要意义;杨硕[15]采用高通量测序技术分析凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群和水体菌群特征,讨论菌群变化的分析利用。【本研究切入点】凡纳滨对虾在我国沿海以及内地均有养殖,对其也有众多的研究[16-20]。为了解不同养殖系统下凡纳滨对虾水体和肠道中微生物菌群结构发生的变化,以微生物多样性研究为基础,利用高通量测序技术进行分析,探讨其重要性。【拟解决的关键问题】利用高通量测序对不同微生物V3+V4区域进行分析,研究两种循环系统下凡纳滨对虾养殖水体以及肠道内微生物的组成,揭示凡纳滨对虾养殖系统中细菌群落结构的某些特征,为相关病原菌的分子检测及实际养殖过程提供参考,为进一步探究凡纳滨对虾生态养殖奠定基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验对象健康、规格一致的凡纳滨对虾(Penaeus vannamei)来自山东潍坊某养殖场,体长约(3.2±0.5) cm,体重约(3.0±0.5) g。养殖池大小均为25 m2,随机放入试验凡纳滨对虾500尾/m2。
1.2 试验设计及养殖条件试验共设2组,对照组(流水系统)与试验组(自行设计循环系统),每组3个平行。
对照组(流水系统):流水养殖模式中养殖池面积25 m2,水深1 m,养殖水源为地下水曝气消毒后经调温直接流入养殖池中,养殖废水直接排放至废水收集池,不进行循环利用。
试验组(循环系统):循环水养殖模式养殖池面积25 m2,水深1 m,养殖水源为地下水曝气消毒后经调温直接流入养殖池中,养殖废水流入沉淀池,经沉淀后流入过滤池,由微滤机去除残饵、粪便等固体代谢物后,进入生物滤池(内含大孔生物载体,在表面及内部固定硝化细菌等微生物)对废水中氨氮、亚硝酸盐等进行调节后再流入养殖池内循环使用,每日添加10%新水作为补充。
试验水源为地下水,水温(25±1)℃,pH值为7.2~7.8,溶氧为5.5~6.5 mg /L,氨氮小于0.4 mg/L。
试验过程中正常管理,24 h充气,每天分别于6:00、14:00、22:00饱食投喂,投饵量以投饵后2 h内吃完为佳;养殖时间共30 d。试验所用基础饲料为大乐饲料有限公司对虾专用配合饲料,主要营养成分如表 1所示。
| 表 1 基础饲料营养成分 Table 1 Nutrient ingredients of basal diet |
试验30 d后分别从不同试验组别中随机取样,每池选取5点位置(四角和中间)分别获取样品后混合均匀,待后续试验。每点取水样量为5 L,混合后用0.45 μm无菌微孔膜进行抽滤,获得微生物菌群样品,-80℃保存备用。凡纳滨对虾每点取20尾,冰上无菌操作获取肠道内容物[21],混合,-80℃保存备用。
1.4 DNA提取、PCR扩增及高通量测序利用QUAGEN试剂盒分别提取水体和肠道细菌基因组总DNA,扩增高可变区(引物319F、806R,参考陈冠舟等[22]方法);一轮扩增之后,在正反向引物两端分别加上不同的adapters和barcodes,再进行扩增;产物纯化之后进行测序。PCR产物用AxyPrepTM Mag PCR Normalizer做归一化处理。
1.5 数据分析本试验针对Illumina MiSeq 2 x 300bp paired-end测序数据进行分析。分析数据库包括RDP11.3、Greengenes13.8、NCBI 16S Microbial和Customized database N/A。分析内容包括原始数据优化及有效优质序列统计、OTU(Operational Taxonomy Unit)聚类统计、OTU比较veen图、Alpha多样性指数(Shannon、Simpson、Chao1)分析、分类丰度分析、物种差异分析及(Un)weighted Unifrac PCoA分析、(Un)weighted Unifrac Tree分析。
原始数据优化及有效优质序列统计:测序获得的原始数据去除reads的barcode和接头序列,将每一对paired-end reads拼接合并成一条更长的tag,去除含有N(N表示无法确定碱基信息)的比例大于5%的tags,去除低质量tags(质量值Q<10的碱基数占整个tag的20%以上),从而获得Clean数据,进行有效序列和优质序列的统计。
OTU聚类统计:采用CD-HIT将序列相似性大于97%的clean tags定为一个OTU,选择其中序列最长的reads作为该OTU的代表序列。OTU比较venn图可用于统计多组样品中所共有和独有的OTU数目,可以比较直观地表现环境样品的OTU数目组成相似性及特异性。
Alpha多样性又为生境内的多样性(Within-habitat Diversity),通常用于度量群落生态中物种的丰富度,是反映丰富度和均匀度的综合指标。本研究基于OTU的结果,计算样品Alpha多样性,包括Shannon、Simpson、Chao1指数。
物种分类丰度分析,是分析多样性的另一种方式。在相似度为0.97的情况下,从纲水平上对不同系统中菌群分布的均匀度进行统计。
物种系统发育进化树,根据数据库分析描述各种生物之间的亲缘关系。
2 结果与分析 2.1 原始数据有效优质序列统计从表 2中可看出,循环系统处理之后凡纳滨对虾养殖水体环境和肠道中优质序列占有效序列的比例明显增加(P<0.05),循环系统可有效优化生境中的微生物生态环境。而且,测序得到的有效序列与优质序列质量很高,可以达到后续微生物多样性的相关分析要求(检测序列长度在300~500 bp)。
| 表 2 有效优质序列统计 Table 2 Statistics of vail and superior sequence |
不同循环系统对于养殖水体环境和养殖对虾肠道微生物多样性产生显著影响。在97%相似性水平上统计,非循环系统中水体样品OTU数量为31 569,凡纳滨对虾肠道样品中OTU数量为21 458;而循环系统中水体样品OTU数量为29 106,凡纳滨对虾肠道样品中OTU数量为19 410(图 1)。从不同养殖系统中样品的共有和独有OTU数目可看出,循环系统更能优化生境中的菌群结构。
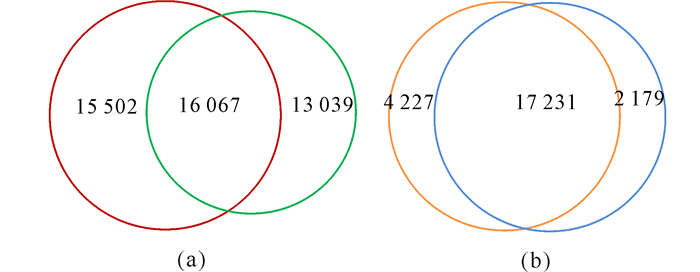
|
不同养殖系统下水体(a)和肠道(b)环境中的OTU分析;红色和橙色环为非循环系统对照组,绿色和蓝色环为循环系统试验组,中间为共有部分 OTU analysis of water in different aquaculture systems; The red and orange rings are control groups in a non-circulatory system, the green and blue rings are experimental groups in a circulatory system, the part in the middle is for the common 图 1 基于OTU数量的veen图 Fig.1 Veen diaqram based on the number of OTU |
Alpha多样性反映了不同养殖系统下水体环境和肠道中的物种丰富度以及差异性。指数越高,物种多样性越高;数值越大,物种越多。在循环系统下,由于特殊的系统结构和处理,生境中物种多样性及分布均匀度均得到优化,可能是在循环过程中除去了一些不必要的杂菌系列(表 3)。
| 表 3 Alpha多样性指数 Table 3 Alpha diversity index |
不同养殖系统影响凡纳滨对虾生境中物种的丰富度及分布情况。从类别上分析,不同样品中细菌序列数为100.0%,均未测序到古菌序列。从纲水平上,循环养殖系统试验组凡纳滨对虾肠道优势菌为蛋白菌门-α-变形菌纲,丰度达57.9%(对照组为38.2%);其次为厚壁菌门-芽孢杆菌纲,丰度为23.9%(对照组为29.2%);再次为拟杆菌门-黄杆菌纲(3.5%)、放线菌门-放线菌纲(1.3%)。而循环水试验组养殖水体中优势菌为α-变形菌纲,丰度达36.9%(对照组为23.8%),γ-变形菌纲丰度为18.3%(对照组为47.3%);其次是黄杆菌纲(16.4%)和放线菌纲(6.6%)。循环养殖系统中凡纳滨对虾肠道和养殖水体中物种丰度相对不同,但也共有一些优势菌纲(表 4)。
| 表 4 丰度统计分析 Table 4 Statistics and analysis of abundance |
如图 2所示,非循环养殖系统水体样品中丰度较高的是γ-变形菌纲、弧菌纲、红细菌目和黄杆菌目,变形菌纲和弧菌纲进化关系较近;而循环养殖系统水体样品中丰度较高的是α-变形菌纲,其次是γ-变形菌纲。两种循环系统中肠道微生物的丰度及关系相似,但非循环系统肠道样品中放线菌纲相对黄杆菌纲丰度高,循环系统中黄杆菌比放线菌丰度高。
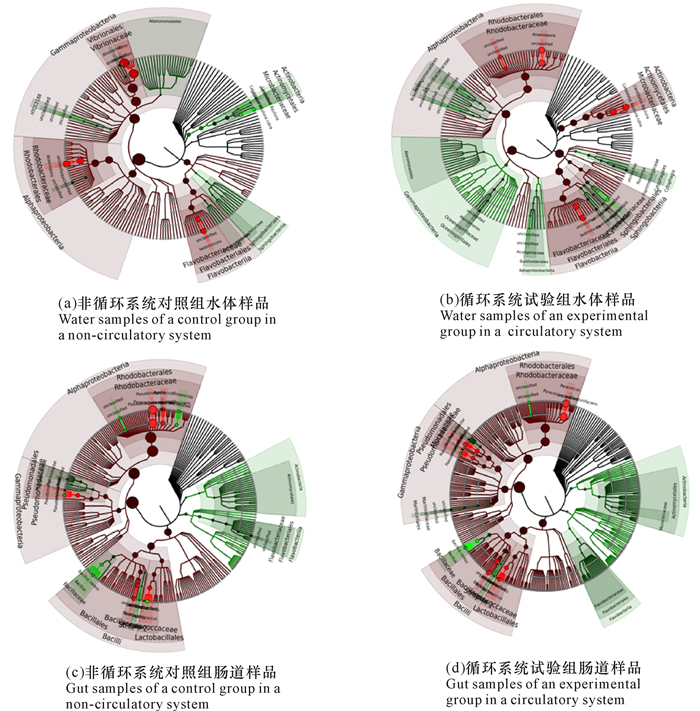
|
环形部分的文字为分类等级,由内到外分类等级为由低到高。节点大小表示丰度高低,绿色覆盖区域表示低丰度,红色覆盖区域表示高丰度 The characters in the ring are classification, the grades from inside to outside are from low to high.Nodes indicate abundance, green coverage area indicates low abundance, red coverage area indicates high abundance 图 2 不同样品中物种系统发育分析 Fig.2 Phylogeny analysis of different sample species |
有关对虾养殖过程中环境或宿主中可培养微生物与其养殖病害相关性早有研究[23],但从微生物角度通过分子技术手段分析水体环境或宿主自身肠道菌群结构变化的报道相对较少。肠道微生物及其菌群结构在动物生长过程中具有重要作用,对虾肠道微生物与对虾营养代谢、能量平衡、免疫防御和胃肠道发育等密切相关,是维持对虾生长过程中肠道内环境稳定的重要因素。近几年高通量测序技术飞速发展,突破传统分析技术上的局限性,能更灵敏地探测环境内丰富的微生物多样性,可实现宏基因组水平上多重样品间的比较分析,扩大微生物相关研究的广度和深度[24]。以往研究发现,变形菌门是养殖海水或高盐湖泊环境中最主要的细菌群体之一[25-26],本研究分析结果也反映了这一规律,在不同养殖系统下水体中优势菌群为变形菌纲,其中α纲和γ纲丰度较高,该结果也与Stevens等[26]的研究结果一致。核心微生物在正常生长环境下能影响和决定宿主自身微生物的组成、群落结构并维持群落平衡[27],且在一定水平上阻止或防御外源生物的侵犯。不同养殖环境、不同养殖对象,其核心微生物的丰度不同,本研究结果显示循环系统可增强核心菌群的丰度,优化养殖生态环境,一定程度上决定养殖对象的健康,进而影响养殖效益。凡纳滨对虾养殖过程中存在潜在的致病菌,循环系统的优势在于改善优势菌的丰度,抑制有害菌的定植,从而创造更加良好的生长环境。
本研究所用循环水养殖系统经过严格筛选,在养殖池及生物净化池中循环流动,从而优化水体中的饵料、粪便及水体中有害生物等外界因素。生物净化池内固定净化水质的有益菌,在生长代谢过程中可抑制水体中氨氮或亚硝酸氮的增加,亦可能与水体中不利于养殖动物生长的有害菌争夺营养,间接预防疾病的发生,最终营造良好的生长环境。而且,从测序结果看,循环系统改善水体中微生物菌群结构,增强优势菌丰度,并进一步改善凡纳滨对虾自身肠道菌群结构,故循环水养殖系统与传统养殖模式相比具有节约养殖用水、养殖效果好等一系列优点,符合建设节约型社会的要求。
4 结论本研究通过高通量测序揭示不同养殖系统中微生物菌群的差异以及多样性。循环水养殖系统优化凡纳滨对虾养殖水体微生物环境,改善凡纳滨对虾自身肠道微生物结构及多样性,对于凡纳滨对虾实际养殖具有指导作用,对阐述养殖过程中微生物和相关疾病的关系具有重要意义。
| [1] |
高权新, 吴天星, 王进波. 肠道微生物与寄主的共生关系研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2010, 22(3): 519-526. GAO Q X, WU T X, WANG J B. Advance in research on symbiotic relationship between intestinal bacterial and their host[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2010, 22(3): 519-526. |
| [2] |
INGERSLEV H C, VON GERSDORFF JØRGENSEN L, STRUBE M L, et al. The development of the gut microbiota in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is affected by first feeding and diet type[J]. Aquaculture, 2014, 424/425: 24-34. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.12.032 |
| [3] |
李存玉, 徐永江, 柳学周, 等. 池塘和工厂化养殖牙鲆肠道菌群结构的比较分析[J]. 水产学报, 2015, 39(2): 245-255. LI C Y, XU Y J, LIU X Z, et al. Comparative analysis of composition, diversity and origin of intestinal bacterial community in pond-and indoor tank-culture Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(2): 245-255. |
| [4] |
李玉宏. 养殖对虾肠道微生物区系的特征与功能[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2013. LI Y H.The characteristic and function research on the intestinal microflora of shrimp[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10264-1014013604.htm |
| [5] |
WANG X H, LI H R, ZHANG X H, et al. Microbial flora in the digestive tract of adult penaeid shrimp (Penaeus chinensis)[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2000, 30(3): 493-498. |
| [6] |
孙昌魁, 冯静, 马桂荣. 海洋微生物多样性的研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2001, 13(3): 97-99. SUN C K, FENG J, MA G R. The progress of studies on marine microorganisms diversity[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2001, 13(3): 97-99. |
| [7] |
DYHRMAN S T, AMMERMAN J W, VAN MOOY B A S. Microbes and the marine phosphorus cycle[J]. Oceanography, 2007, 20(2): 110-116. |
| [8] |
夏苏东, 李勇, 王文琪, 等. 养殖自污染因子对虾蟹健康的影响及其机理与控制[J]. 水产科学, 2009, 28(6): 355-360. XIA S D, LI Y, WANG W Q, et al. The mechanism and control of self-pollution factors affecting health of prawn and crab[J]. Fisheries Science, 2009, 28(6): 355-360. |
| [9] |
REDDY-LOPATA K, AUERSWALD L, COOK P. Ammonia toxicity and its effect on the growth of the South African abalone Haliotis midae Linnaeus[J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 261(2): 678-687. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.06.020 |
| [10] |
DAVIDSON J, GOOD C, WELSH C, et al. Abnormal swimming behavior and increased deformities in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss cultured in low exchange water recirculating aquaculture systems[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2011, 45(3): 109-117. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2011.08.005 |
| [11] |
DRENGSTIG A, BERGHEIM A. Commercial land-based farming of European lobster (Homarus gammarus L.) in recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) using a single cage approach[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2013, 53: 14-18. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2012.11.007 |
| [12] |
谭建, 罗坤, 栾生, 等. 循环水养殖系统在凡纳滨对虾种虾养殖中的应用效果初探[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(4): 63-70. TAN J, LUO K, LUAN S, et al. Preliminary application of the recirculating aquaculture system in Litopenaeus vannamei breeding[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(4): 63-70. |
| [13] |
李祎, 郑伟, 郑天凌. 海洋微生物多样性及其分子生态学研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(4): 655-668. LI Y, ZHENG W, ZHENG T L. Advances in research of marine microbial diversity and molecular ecology[J]. Microbiology China, 2013, 40(4): 655-668. |
| [14] |
薛明, 何瑶瑶, 邱孟德, 等. 高通量测序分析凡纳滨对虾育苗期水体菌群结构特征[J]. 水产学报, 2017, 41(5): 785-794. XUE M, HE Y Y, QIU M D, et al. Characterization of aquatic bacterial community of Litopenaeus vannamei larvae during hatchery period with high-throughput sequencing[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(5): 785-794. |
| [15] |
杨硕. 凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群分析及其利用[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2016. YANG S.Analysis and utilization of intestinal flora in Litopenaeus vannamei[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10057-1017058330.htm |
| [16] |
张吕平, 胡超群, 罗鹏, 等. 抗生素对于对虾苗池水体细菌区系的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(10): 2551-2557. ZHANG L P, HU C Q, LUO P, et al. Effects of antibiotics on bacterial community in shrimp hatchery system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(10): 2551-2557. |
| [17] |
WEN C Q, XUE M, LIANG H F, et al. Evaluating thepotential of marine Bacteriovorax sp.DA5 as a biocontrol agent against vibriosis in Litopenaeus vannamei larvae[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2014, 173(1/2): 84-91. |
| [18] |
罗鹏, 胡超群, 张吕平, 等. 凡纳滨对虾海水养殖系统内细菌群落的PCR-DGGE分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2009, 16(1): 31-38. LUO P, HU C Q, ZHANG L P, et al. PCR-DGGE analysis of bacterial communities in marine Litopenaeus vannamei culture system[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2009, 16(1): 31-38. |
| [19] |
盖春蕾, 张元发, 叶海斌. 凡纳滨对虾体内大黄苷的药代动力学特征[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2016, 32(4): 282-287. GAI C L, ZHANG Y F, YE H B. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of rhein in the body of Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2016, 32(4): 282-287. |
| [20] |
易湘茜, 孙恢礼, 潘剑宇. 凡纳滨对虾生命周期环境影响模型分析评价研究[J]. 广西科学, 2014, 21(3): 306-312. YI X X, SUN H L, PAN J Y. The evaluation of the model of life cycle assessment (LCA) in Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2014, 21(3): 306-312. |
| [21] |
唐杨, 刘文亮, 宋晓玲, 等. 饲料中补充蜡样芽孢杆菌对凡纳滨对虾生长及其肠道微生物组成的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2017, 41(5): 766-774. TANG Y, LIU W L, SONG X L, et al. Effects of dietary with Bacillus cereus on the growth rate and intestinal microflora of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(5): 766-774. |
| [22] |
陈冠舟, 张白鹭, 纪梦梦, 等. 高通量测序探究啮食聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料黄粉虫的肠道菌群结构[J/OL]. 微生物学通报, (2017-06-06)[2017-08-21]. http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1996.Q.20170606.1242.006.html. CHEN G Z, ZHANG B L, JI M M, et al.Gut microbiotia of polystyrene-eating mealworms analyzed by high-throughput sequencing[J/OL]. Microbiology China, (2017-06-06)[2017-08-21]. http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1996.Q.20170606.1242.006.html. |
| [23] |
VANDENBERGHE J, VERDONCK L, ROBLESAR OZARENA R, et al. Vibrios associated with Litopenaeus vannamei larvae, postlarvae, broodstock, and hatchery probionts[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(6): 2592-2597. |
| [24] |
WU L Y, WEN C Q, QIN Y J, et al. Phasing amplicon sequencing on Illumina Miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2015, 15: 125. DOI:10.1186/s12866-015-0450-4 |
| [25] |
DEMERGASSO C, CASAMAYOR E O, CHONG G, et al. Distribution of prokaryotic genetic diversity in athalassohaline lakes of the Atacama Desert, Northern Chile[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2004, 48(1): 57-69. DOI:10.1016/j.femsec.2003.12.013 |
| [26] |
STEVENS H, STVBNER M, SIMON M, et al. Phylogeny of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes from oxic habitats of a tidal flat ecosystem[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2005, 54(3): 351-365. DOI:10.1016/j.femsec.2005.04.008 |
| [27] |
SHADE A, HANDELSMAN J. Beyond the Venn diagram:The hunt for a core microbiome[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 14(1): 4-12. DOI:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33 


