2. 广西科学院广西近海海洋环境科学重点实验室,广西南宁 530007
2. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, Guangxi Academy of Sciences, Nanning, Guangxi, 530007, China
【研究意义】沉积物是水环境中重金属的源与汇,在物理、化学和生物作用下,沉积物内的重金属易再次释放进入水中,造成二次污染[1]。涠洲岛珊瑚礁主要分布于北部、东部和西南部沿岸 。珊瑚礁不仅是海洋中最大的生态系统,也是地球上除热带雨林生态系统外的第二大生态系统,其对于海洋生物多样性保护及维护区域和全球生态健康均具有重要作用,是海洋环境健康的重要指示物 。珊瑚礁的存活和生长与海域水体重金属污染状况关系密切 ,当海水中重金属超过一定质量浓度时就会影响到珊瑚礁的生长发育和存活 。因此,对涠洲岛沉积物中重金属含量进行研究有利于了解该海域水体重金属污染状况,可为该海区珊瑚及其它环境资源保护和可持续发展提供科学依据。【前人研究进展】据1999年邱绍芳[10]的调查,涠洲岛附近海域的水质和底质均未发现污染,环境良好。之后学者们研究发现该岛潮滩多数地区存在Cu污染,个别地区存在As污染,附近海域石油类和重金属Pb超一类海水水质标准,水质呈轻度污染状态 。2015年杨华等[13]调查了涠洲岛附近有珊瑚群落发育的海域,发现部分站点Pb和Hg质量浓度略高于一类海水水质标准,认为Hg是珊瑚生长区的主要生态风险因子。综上可见,涠洲岛海域重金属污染呈加剧趋势,极可能影响珊瑚礁的生长存活。【本研究切入点】目前关于涠洲岛海域重金属研究仍较缺乏,为了保护该岛珊瑚及其它环境资源不受到污染破坏,有必要加强该方面研究。【拟解决的关键问题】考虑到涠洲岛海域重金属分布具有南高北低的特点[13],本研究以该岛西面和西南面作为研究区域,采用瑞典科学家Hakanson[14]潜在生态风险评价方法和德国科学家Muller[15]提出的地累积指数法对该区域重金属含量进行综合评价。
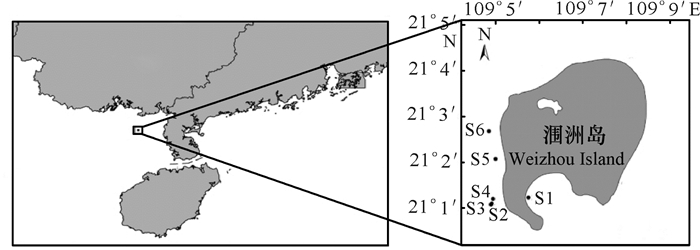
1 材料与方法 1.1 调查站位于2014年在广西涠洲岛6个采样点(S1、S2、S3、S4、S5、S6)进行海水沉积物样品采集(图 1),具体操作参考《海洋监测规范》(GB 17378—2007)[16]。
|
图 1 采样地点 Fig.1 Sampling sites |
单因子污染系数Cfi反映沉积物中某重金属i的污染程度。计算公式如下:
| $ C_f^i = C_s^i/C_n^i, $ | (1) |
式中,Csi为某重金属元素i的实测数值,Cni采用北部湾海底沉积物重金属元素背景值(表 1)[17]。Cfi<1为低污染,1≤Cfi<3为中污染,3≤Cfi<6为较高污染,Cfi≥6为高污染[14]。
| 表 1 北部湾重金属元素的背景参考值及毒性响应系数 Table 1 Background level and toxic coefficient for heavy metals in Beibu Gulf |
Cs 是指单因子污染系数之和,公式如式(2)所示,综合污染指数分级标准见表 2。
| $ {C_s} = \sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^5 {C_f^i}。$ | (2) |
| 表 2 综合污染指数分级标准 Table 2 Cs classification standard |
单个重金属的潜在生态风险系数Efi反映重金属的毒性水平和生物对其污染的敏感程度(表 3),公式为
| $ E_f^i = T_f^i \times C_f^i, $ | (3) |
| 表 3 单个重金属潜在生态风险系数及多种重金属潜在生态风险指数的危害等级 Table 3 Pollution grade for the single heavy metal and potential ecological risk index RI |
式中,Tfi为重金属的毒性响应系数(表 1),Cfi为单因子污染系数。
1.2.4 多种重金属潜在生态风险指数RI为沉积物中多种重金属潜在生态风险指数,其分级见表 3。
| $ RI = \sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {E_f^i}。$ | (4) |
地累积指数是德国科学家Muller[15]提出的针对沉积物中重金属污染程度评价的常用指标,能直观地反映重金属的累积程度,公式为
| $ {I_{{\rm{geo}}}} = {\rm{lo}}{{\rm{g}}_2}({C_n}/k{B_n}), $ | (5) |
式中:Igeo为地累积指数;Cn为第n种重金属在沉积物中的测定值(mg·kg-1);k通常设为常数,取值1.5;Bn为沉积岩中第n种元素的地球环境背景值(mg·kg-1),本研究采用北部湾海底沉积物重金属元素背景值作为参照值(表 1)。Igeo和污染程度关系见表 4。
| 表 4 Igeo与重金属污染程度的关系 Table 4 Correlations between Igeo and heavy metals pollution degree |
涠洲岛西面及西南面水域重金属含量如表 5所示,均值大小依次为Cd<Cu<Pb<Cr<Zn。参考《海洋沉积物质量》(GB 18668-2002)Ⅰ类沉积物标准[18],研究区内所测重金属含量均未超出Ⅰ类标准值。其中,除Cd未检出外,Pb的标准差最小,分布相对均匀,Cu、Cr次之,Zn离散程度最高,分布最为不均。Cu含量峰值发生在采样点S5,Pb发生在采样点S3,Zn则有多个峰值,分别出现在采样点S3和S5。
| 表 5 2014年涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物重金属含量特征 Table 5 Heavy metal content in the sediments of west and southwest of Weizhou Island in 2014 |
据公式(1)计算出每个采样点5种重金属的单因子污染系数,从数据上看所有单因子污染系数 < 1,单因子污染系数均值排列顺序为Cd < Cr < Pb < Zn < Cu(表 5)。所有站位重金属元素的综合污染指数Cs<5,污染程度分级均为低水平(表 6)。
| 表 6 2014年涠洲岛西面及西南面海域沉积物重金属污染程度及分布状况 Table 6 Heavy metal pollution and its distribution in sediments in the west and southwest seas of Weizhou Island in 2014 |
以北部湾海底沉积物重金属元素背景值作为标准(表 1),据公式(3)和(4)计算出每个采样点的潜在生态风险指数(表 7)。从生态危害的角度看,各重金属元素的潜在生态风险系数Efi呈Cd < Zn < Cr < Pb < Cu,对应均值均远小于40;各站位多种重金属潜在生态风险指数RI为0.86~7.97,远小于150,因此,涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物重金属生态风险分级属于“轻微生态危害”。
| 表 7 2014年涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数与分级 Table 7 Potential ecological risk index and classification of heavy metals in sediments in west and southwest of Weizhou Island in 2014 |
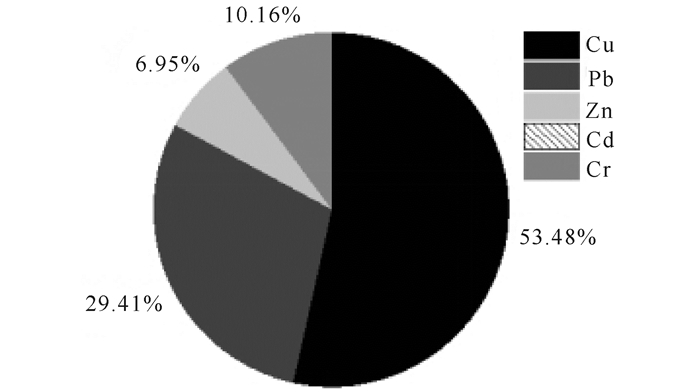
总的来说,重金属Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Cr对本研究海域RI的如图 2所示。具体到各采样区域,除S2站点Pb对RI贡献最大外,其它站点Cu的贡献率最大。可见Cu是涠洲岛西面及西南面重金属污染的主要风险因子,对生态环境的潜在危害较大。
|
图 2 不同重金属对RI的贡献率 Fig.2 Contribution rate to risk index from different heavy metals |
涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物重金属的地累积指数排序分别为Cd<Cr<Pb<Cu<Zn,污染等级均为0级(表 8),污染程度为无污染。
| 表 8 2014年涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物重金属的Igeo及污染等级 Table 8 Igeo and pollution levels of heavy metals in sediments in west and southwest of Weizhou Island in 2014 |
重金属具有生物富集、生物放大及难解降等特点,而绝大部分重金属会很快由水相转为固相,研究表明,水相中重金属的含量少、随机性强且分布规律不固定,而沉积物中重金属累积的含量比水体中高很多倍,且具有明显的分布规律性[19]。因此,对沉积物中重金属进行污染评价有助于评估研究区域的环境质量状况。涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物中各重金属单因子污染系数和综合污染指数、单重金属潜在生态风险系数、多种重金属潜在生态风险指数、地累积指数都处于低污染水平,说明涠洲岛西面及西南面目前重金属污染轻微。单因子污染系数和潜在生态风险系数评价结果存在差异,分析原因,可能是由于个别重金属元素的亲颗粒性导致它们对海域生物造成的毒性有所差异,使污染程度和所造成生态危害程度之间不完全一致[1, 20]。
涠洲岛海域沉积物的历史数据表明(表 9),重金属含量均值和变化范围长期处于清洁水平内,各元素均未达到污染水平。2006年除Cu含量的均值比1999年高,其他元素含量则较1999年低,本研究中所有元素含量均值均较2006年低,说明不考虑采样站位差异,涠洲岛海域沉积物重金属环境质量状况呈持续好转趋势。与广西沿海其它海域相比(表 10),涠洲岛西面及西南面沉积物的重金属含量较低,在北部湾海域最低,污染较小,其数值更接近于北海所测数据。由于防城港、钦州湾区域的港口、工业区较为密集,海域沉积物重金属含量相对较高。
| 表 9 往年涠洲岛海域沉积物重金属含量 Table 9 Heavy metals in sediments of Weizhou Island in previous years |
| 表 10 涠洲岛与广西沿海其他海域沉积物重金属含量比较 Table 10 Comparison of heavy metals concentration in sediment of Weizhou Island with other seawaters in Guangxi |
涠洲岛西面及西南面海域沉积物重金属均值依次为Cd<Cu<Pb<Cr<Zn,分别对应未检出、3.02 mg·kg-1、3.19 mg·kg-1、6.47 mg·kg-1、10.10 mg·kg-1,含量范围分别为未检出、0.95~8.29 mg·kg-1、2.68~4.07 mg·kg-1、1.81~18.46 mg·kg-1、ND~34.59 mg·kg-1。各重金属单因子污染系数均 < 1,所有站位重金属综合污染指数 < 5,污染程度均属于“低水平”。单个及多种重金属生态风险分级均为“轻微”,其中Cu是引发生态风险的主要元素。地累积指数亦表明该海域各重金属污染程度均为0级。总体来说,涠洲岛西面及西南面海域沉积物重金属含量与污染程度较广西沿海其他海域低。涠洲岛西面及西南面海域底质尚属清洁。
| [1] |
贾振邦, 梁涛, 林健枝, 等. 香港河流重金属污染及潜在生态危害研究[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 1997, 33(4): 485-492. JIA Z B, LIANG T, LIN J Z, et al. Study on heavy metal contamination and potential ecological risk in Hong Kong rivers[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 1997, 33(4): 485-492. |
| [2] |
梁文, 黎广钊. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁分布特征与环境保护的初步研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2002, 15(6): 5-7, 16. LIANG W, LI G Z. Preliminary study on characteristics of coral reef distribution and environmental protection in Weizhou Island[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 15(6): 5-7, 16. |
| [3] |
王宁. 涠洲岛珊瑚骨骼微量元素的时、空特征及其控制因素[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017. WANG N. The temporal and spatial characteristics and controlling factors of coral skeleton elements from Weizhou Island[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017. |
| [4] |
MOBERG F, FOLKE C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems[J]. Ecological Economics, 1999, 29: 215-233. DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00009-9 |
| [5] |
张乔民, 余克服, 施祺, 等. 全球珊瑚礁监测与管理保护评述[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2006, 25(2): 71-78. ZHANG Q M, YU K F, SHI Q, et al. A review of monitoring, conservation and management of global coral reefs[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2006, 25(2): 71-78. |
| [6] |
史海燕, 刘国强. 广西北海涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域生态环境现状与评价[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2012(14): 11-12. SHI H Y, LIU G Q. Ecological environment status and assessment of Weizhou Island coral reefs in North Sea of Guangxi[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2012(14): 11-12. |
| [7] |
刘文新, 栾兆坤, 汤鸿霄. 乐安江沉积物中金属污染的潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 1999, 19(2): 206-211. LIU W X, LUAN Z K, TANG H X. Environmental assessment on heavy metal pollution in the sediments of Le An River with potential ecological risk index[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1999, 19(2): 206-211. |
| [8] |
JEZIERSKA B, ŁUGOWSKA K, WITESKA M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review)[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 35(4): 625-640. DOI:10.1007/s10695-008-9284-4 |
| [9] |
THOMPSON E L, TAYLOR D A, NAIR S V, et al. A proteomic analysis of the effects of metal contamination on Sydney Rock Oyster (Saccostrea glomerata) haemolymph[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2011, 103(3/4): 241-249. |
| [10] |
邱绍芳. 涠洲岛附近海域水质和底质环境的分析与评价[J]. 广西科学院学报, 1999, 15(4): 170-173. QIU S F. Analysis and evaluation of substrate environment and water quality of the sea area around Weizhou Island[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 1999, 15(4): 170-173. |
| [11] |
唐璐璐, 陈志华, 印萍, 等. 涠洲岛潮滩表层沉积物中重金属的空间分布及其环境质量评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2009(2): 124-130. TNAG L L, CHEN Z H, YIN P, et al. Heavy metals' spatial distribution of the intertidal surface sediments in Weizhou Island and its environment quality evaluation[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009(2): 124-130. |
| [12] |
谭趣孜, 梁文. 广西涠洲岛附近海域水质现状评价与分析[J]. 广西轻工业, 2011, 27(10): 107-108. TAN Q Z, LIANG W. Evaluation and analysis of water quality status near Weizhou Island in Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry, 2011, 27(10): 107-108. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-2673.2011.10.056 |
| [13] |
杨华, 王少鹏, 余克服, 等. 南海北部珊瑚生长区海水重金属污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 253-260. YANG H, WANG S P, YU K F, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in seawater of coral growing regions in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(2): 253-260. |
| [14] |
HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. DOI:10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 |
| [15] |
MULLER G. Index of Geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2: 108-118. |
| [16] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋监测规范: GB 17378. 5—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. The specification for marine monitoring: GB 17378. 5—2007[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2007. |
| [17] |
唐博, 龙江平, 金路, 等. 珠江口和北部湾附近海域沉积物重金属生态风险比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. TANG B, LONG J P, JIN L, et al. The contrast of heavy metals' ecological risks in marine sediments between the Beibu Gulf and the Pearl River Delta[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. DOI:10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.03.010 |
| [18] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋沉积物质量: GB 18668—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002. General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Marine sediment quality: GB 18668—2002[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2002. |
| [19] |
贾振邦, 周华, 赵智杰, 等. 应用地积累指数法评价太子河沉积物中重金属污染[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2000, 36(4): 41-44. JIA Z B, ZHOU H, ZHAO Z J, et al. The application of the index of Geoaccumulation to evaluate heavy metal pollution in sediments in the Benxi section of the Taizi River[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2000, 36(4): 41-44. |
| [20] |
王志峰, 王建春, 程凤莲, 等. 北部湾潮间带沉积物中重金属和多氯联苯的分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(9): 1293-1302. WANG Z F, WANG J C, CHENG F L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls in the intertidal sediments along the Beibu Bay[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(9): 1293-1302. |
| [21] |
甘华阳, 郑志昌, 梁开, 等. 广西北海近岸海域表层沉积物的重金属分布及来源分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2010, 29(5): 698-704. GAN H Y, ZHENG Z C, LIANG K, et al. Spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in surface sediment from near-shore area of Beihai, Guangxi[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2010, 29(5): 698-704. |
| [22] |
姜发军, 尹闯, 张荣灿, 等. 2010年冬季广西北部湾近岸海域表层海水和沉积物中重金属污染现状及评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2013, 32(6): 824-830. JIANG F J, YIN C, ZHANG R C, et al. Pollution assessment and evaluation of heavy metals in the sea water and surface sediments of Guangxi Beibu Gulf coast in winter 2010[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(6): 824-830. |
| [23] |
田海涛, 胡希声, 张少峰, 等. 茅尾海表层沉积物中重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2014, 33(2): 187-191. TIAN H T, HU X S, ZHANG S F, et al. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Maowei Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2014, 33(2): 187-191. |
| [24] |
吴文成, 任露陆, 蔡信德, 等. 茅尾海沉积物重金属空间分布特征与生态风险[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(2): 147-156. WU W C, REN L L, CAI X D, et al. Spatial pattern and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from Maowei Sea, Southern China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(2): 147-156. |
 2018, Vol. 25
2018, Vol. 25 


